

You know, thermoPlastic Welding is really taking off these days and becoming a key player in how things are made and built. It offers some pretty great perks—like creating seamless joints that are also strong and flexible, which can be a real game-changer depending on what you’re working on. I read somewhere that, according to MarketsandMarkets, the global market for thermoplastic welding is expected to hit about 4.5 billion dollars by 2026. That's pretty impressive, especially since it’s growing at around 6.2% annually. The big reasons? New and better welding techniques are popping up all the time, and there’s definitely a push for lighter, more efficient materials—think cars, planes, and construction projects.
Dr. James Atherton, who’s kind of a go-to expert in this field, mentioned once, “The versatility and efficiency of thermoplastic welding really allow for faster production and top-notch quality, meeting even the toughest engineering standards today.” As companies and industries keep leaning toward more sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing methods, thermoplastic welding is only going to get more important. It’s pretty amazing how it can connect parts so solidly without messing with the material’s integrity. Honestly, I think this technique is definitely going to be a big deal moving forward in lots of different areas.

Thermoplastic welding is a process that involves joining thermoplastic materials through the application of heat and pressure. This technique is particularly effective because thermoplastics soften when heated, allowing them to meld seamlessly with other parts. Once cooled, the materials harden, creating a strong bond that maintains the integrity of the original materials. The fundamental principle behind thermoplastic welding lies in the ability of these materials to be re-formed and reshaped without compromising their structural properties, making them ideal for various applications across multiple industries.
Key concepts in thermoplastic welding include the methods employed, such as hot air welding, ultraSonic Welding, and laser welding, each offering unique advantages depending on the specific requirements of the project. For instance, hot air welding provides a robust joint for larger pieces, while ultrasonic welding is particularly suitable for delicate components requiring precise joining. Understanding these techniques allows engineers and manufacturers to select the most appropriate method for their specific applications, whether in automotive, aerospace, or medical device manufacturing, ensuring strong and durable connections while optimizing production efficiency.
Thermoplastic welding has emerged as a vital technique in modern manufacturing, delivering several significant benefits that contribute to efficiency and cost-effectiveness. According to a report from the American Welding Society, the thermoplastic welding market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2021 to 2027, indicating increasing adoption across various industries. This form of welding offers a unique advantage in joining materials that can be reshaped and reused, enhancing sustainability. Manufacturers can significantly reduce material waste by using thermoplastic materials that allow for recycling, thus promoting a circular economy.
In terms of versatility, thermoplastic welding can be adapted to various applications, including automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. Industry studies suggest that using thermoplastic materials can lead to reductions in weight by up to 30% for automotive components, improving fuel efficiency and overall performance. Furthermore, the speed at which thermoplastic welding can be executed—often faster than traditional welding techniques—leads to shorter production cycles and enhances productivity. The ability to join complex geometries also expands the design possibilities for engineers and designers, making thermoplastic welding an essential tool for advancing innovative manufacturing solutions.

Thermoplastic welding is a crucial technique used in various industries to join thermoplastic materials efficiently and effectively. Several common methods are employed in thermoplastic welding processes, each with its unique applications and advantages. One of the most widely used techniques is hot air welding, where a stream of hot air is directed at the surfaces to be joined, melting the materials together. This method is particularly effective for larger components, as it allows for a degree of flexibility and control over the welding process.
Another prevalent technique is ultrasonic welding, which utilizes high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to generate heat at the joint interface, causing the thermoplastic to melt and fuse. This method is ideal for precision applications, often seen in the automotive and electronics industries, due to its ability to create strong bonds with minimal thermal distortion. Additionally, laser welding is increasingly used for its speed and accuracy, particularly in applications where high-quality seams are essential, such as in the medical device sector. Each of these techniques showcases the versatility of thermoplastic welding, making it an invaluable process in modern manufacturing.
Thermoplastic welding is increasingly adopted across various industries due to its versatility and efficiency. One of the primary sectors benefitting from this technique is the automotive industry, where it is utilized to join components made from thermoplastic materials. This process enables manufacturers to create lightweight and durable parts, significantly contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions in vehicles. Furthermore, the speed of thermoplastic welding allows for streamlined production lines, thereby enhancing overall productivity.
Another prominent application of thermoplastic welding is in the construction sector, particularly for joining plastic membranes in roofing and waterproofing systems. The ability to create strong, watertight seals is crucial in these applications, ensuring longevity and reliability in structures. Additionally, the medical device industry leverages thermoplastic welding for the assembly of various components, including tubing and enclosures. This technique allows for contamination-free joining processes, which is essential for maintaining the integrity and safety of medical products. Overall, industries utilizing thermoplastic welding benefit from enhanced performance characteristics and improved manufacturing processes.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Thermoplastic welding is a process where thermoplastic materials are joined together using heat and pressure. |
| Benefits | High durability, resistance to chemicals, quick processing time, and flexibility in design. |
| Common Techniques | Ultrasonic welding, hot plate welding, and vibration welding. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, medical devices, consumer electronics, and packaging materials. |
| Industries Utilizing It | Manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, and construction. |
| Environmental Impact | Often utilizes recyclable materials, contributing to sustainable practices. |
Thermoplastic welding is a method that stands out due to its unique characteristics and advantages compared to traditional welding techniques. Unlike arc or gas welding, which often involves melting the base materials to join them, thermoplastic welding utilizes heated tools or friction to soften the thermoplastic materials, allowing them to bond upon cooling. This approach results in lower thermal distortion and reduced risk of damaging the base materials, making it ideal for applications where precision and material integrity are crucial.
Moreover, thermoplastic welding offers superior flexibility and adaptability in various environments. For instance, when juxtaposed with resistance welding or laser welding, thermoplastic techniques often require less setup and can be performed at lower temperatures. This not only conserves energy but also expands the range of thermoplastics that can be effectively welded. Additionally, the ability to replace components easily without extensive reworking is a significant advantage over traditional welding methods, making it an attractive choice for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, where modular design is increasingly favored.
Thermoplastic welding has emerged as a crucial technique in various industries, providing strong and durable joints for thermoplastic materials. However, safety considerations and best practices are essential to ensure effective and safe welding processes. According to a report by the American Welding Society, improper handling of thermoplastic welding equipment can lead to workplace accidents, emphasizing the importance of proper training and safety protocols. Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, face shields, and respiratory protection should always be utilized to safeguard workers from hazardous fumes and potential heat exposure.
Furthermore, maintaining a clean and well-ventilated workspace is critical in thermoplastic welding operations. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health highlights that inadequate ventilation can lead to the buildup of harmful fumes emitted during the welding process. Implementing effective ventilation systems and regularly monitoring air quality can significantly reduce health risks for workers. In addition, it is vital to adhere to equipment manufacturer specifications and recommendations during setup and operation to minimize the chances of equipment failure or accidents. Establishing a comprehensive safety training program is essential to educate employees on the risks and the best practices associated with thermoplastic welding, ensuring a safer working environment while optimizing productivity.
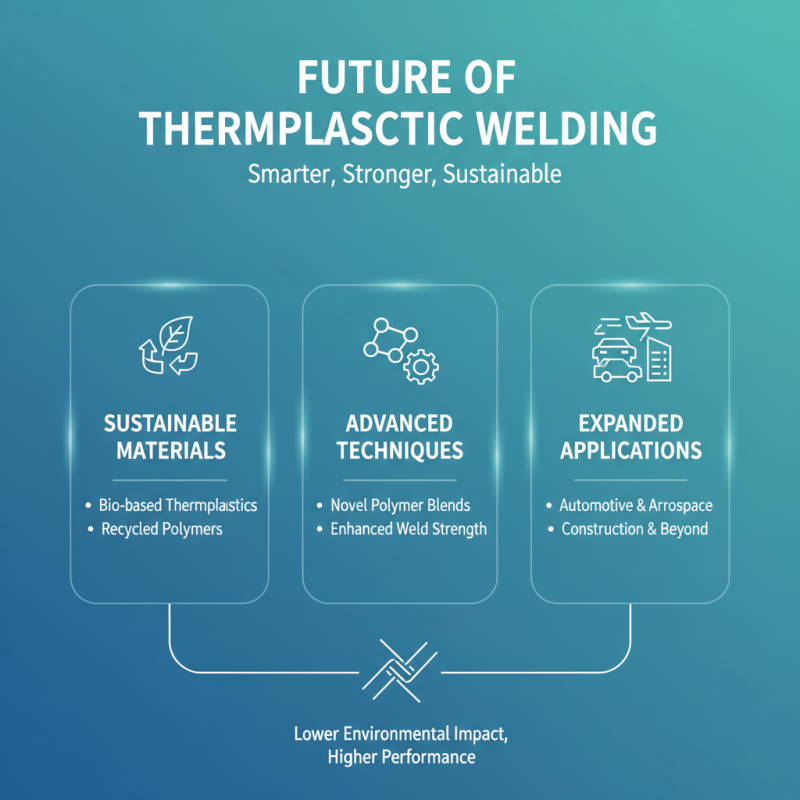
The future of thermoplastic welding technology is poised for remarkable advancements driven by innovations in materials and techniques. As industries prioritize sustainability, the development of bio-based and recycled thermoplastics is gaining momentum. These materials not only provide a lower environmental impact but also enhance the performance of welded products. Research into novel polymer blends offers opportunities to create stronger, more durable welds, thereby expanding the potential applications of thermoplastic welding in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Moreover, the integration of automation and robotics is transforming thermoplastic welding processes. Automated welding systems enable more precise and efficient production, reducing labor costs and increasing throughput. Advanced monitoring technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, provide real-time feedback during welding operations, ensuring optimal quality control. These innovations not only streamline manufacturing processes but also open new avenues for high-performance thermoplastic components in emerging technologies, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
: Thermoplastic welding is a process that involves joining thermoplastic materials using heat and pressure, allowing them to soften and meld together. Once cooled, they create a strong bond while maintaining their structural integrity.
The primary advantages include the ability to create strong and durable joints, the capability of thermoplastics to be re-formed and reshaped, and the versatility of methods such as hot air welding, ultrasonic welding, and laser welding for various applications.
Essential safety measures include using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and face shields, ensuring adequate ventilation to avoid harmful fumes, and adhering to equipment manufacturer specifications.
Common methods of thermoplastic welding include hot air welding, which is suitable for larger pieces, ultrasonic welding for delicate components, and laser welding, each with unique advantages tailored to specific project requirements.
Improving workplace safety involves proper training for workers, implementing effective ventilation systems, and establishing comprehensive safety training programs to educate employees about risks and best practices.
Future trends include advancements in materials such as bio-based and recycled thermoplastics, the integration of automation and robotics for enhanced efficiency, and the use of advanced monitoring technologies for better quality control.
Ventilation is crucial as inadequate airflow can lead to the buildup of harmful fumes emitted during the welding process, posing health risks to workers. Effective ventilation systems help mitigate these risks.
Automation enhances thermoplastic welding processes by enabling precise control, increasing production efficiency, reducing labor costs, and facilitating real-time monitoring for quality assurance.
The choice of thermoplastic material can significantly affect the welding process, as different materials may require specific welding techniques and conditions to achieve optimal bond strength and performance.
Thermoplastic welding is commonly utilized in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing, where strong and reliable joints are essential.
Thermoplastic welding is a versatile and efficient technique used in various manufacturing processes, allowing for the joining of thermoplastic materials through heat and pressure. This method offers several benefits, including strong and durable joints, the ability to create complex shapes, and minimal environmental impact due to its recyclability. Common techniques such as ultrasonic welding, hot air welding, and friction welding are employed across numerous industries, from automotive to healthcare, facilitating the development of innovative products.
In comparison to other welding methods, thermoplastic welding stands out for its ability to create seamless and highly resistant joints without the need for additional materials. However, it is essential to adhere to safety considerations and best practices to ensure effective and safe operations. As technology evolves, future trends in thermoplastic welding may introduce new techniques and applications, further enhancing its role in modern manufacturing.








