

You know, when it comes to modern manufacturing these days, Thin Film Welding really can’t be overlooked. As industries push for more precision and efficiency, there’s definitely been a big jump in the need for new, innovative welding techniques. I came across a report from Allied Market Research that predicts the global market for thin film tech will hit around $20 billion by 2027, growing at about 15% annually since 2020. That’s pretty impressive and really shows just how crucial thin film welding has become across different sectors—everything from electronics to renewable energy.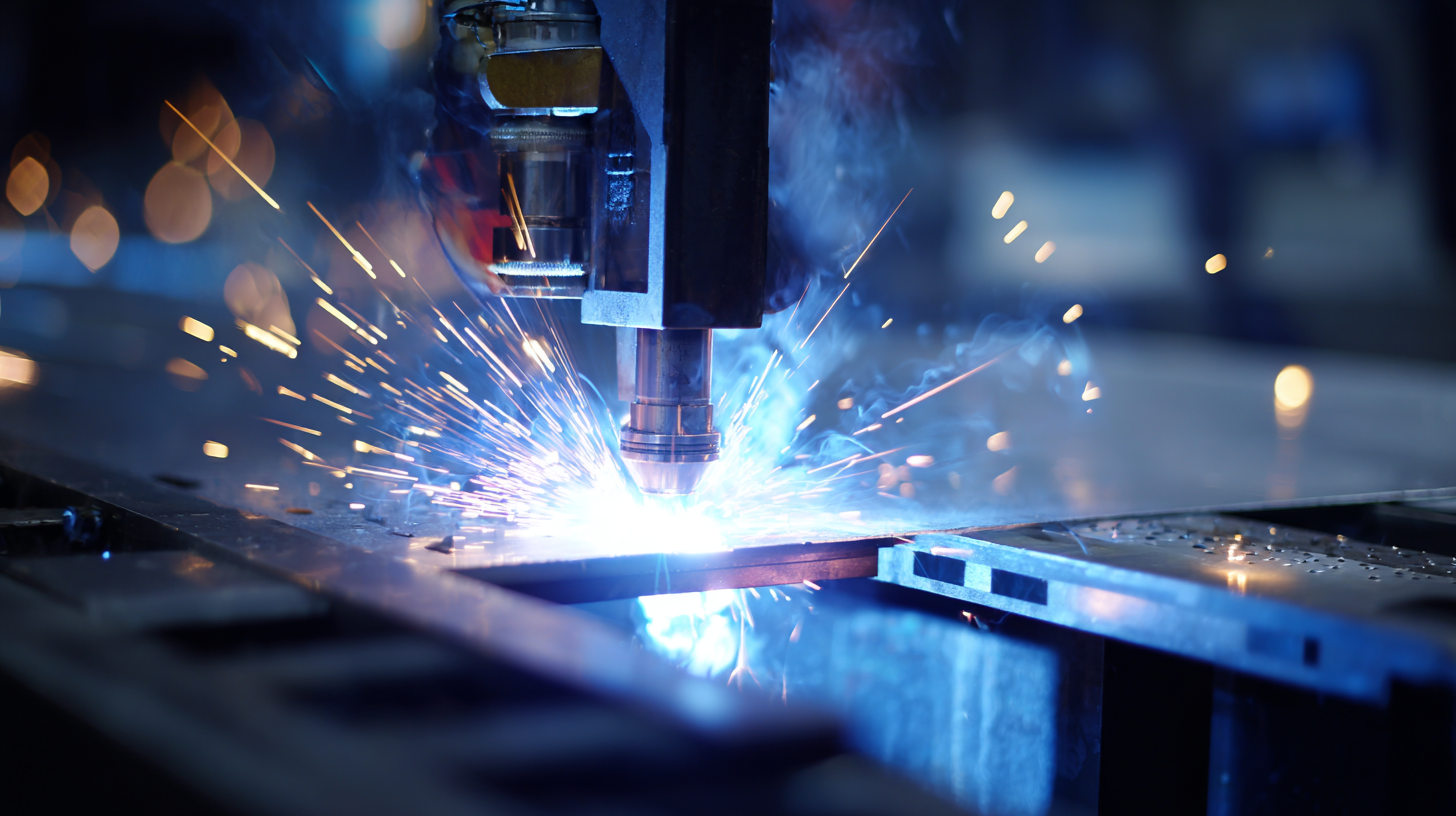 Dr. Emily Carter, who’s a leading expert in advanced manufacturing—and honestly someone I really respect—made a good point about this. She said, “Thin Film Welding not only makes the materials stronger and better, but it also cuts down on costs and reduces waste.” That really hits home, especially with the whole trend leaning toward more sustainable manufacturing practices. It’s great to see companies adopting methods that are better for the environment but also boost product quality.
Dr. Emily Carter, who’s a leading expert in advanced manufacturing—and honestly someone I really respect—made a good point about this. She said, “Thin Film Welding not only makes the materials stronger and better, but it also cuts down on costs and reduces waste.” That really hits home, especially with the whole trend leaning toward more sustainable manufacturing practices. It’s great to see companies adopting methods that are better for the environment but also boost product quality.
As manufacturing keeps evolving, getting on board with thin film welding is pretty much essential if a company wants to stay competitive. Its ability to create lightweight yet tough products sets manufacturers up well for the future, all while keeping sustainability and efficiency front and center.
Thin film welding has emerged as a crucial technique in modern manufacturing, delivering unique advantages that enhance production efficiency and product quality. One of the key benefits is its ability to facilitate precise control over the welding process, minimizing defects and ensuring strong bonds between materials. This precision is particularly significant in industries such as electronics and aerospace, where reliability is paramount.
Tips: Always maintain optimal temperature control during the thin film welding process to prevent degradation of materials. Additionally, consider pre-treating surfaces to improve adhesion quality, which can lead to better overall performance of the final product.
Another significant advantage of thin film welding is its versatility. The technique can be employed across a diverse range of materials, including metals, polymers, and ceramics, making it suitable for various applications in advanced manufacturing. Moreover, thin film welding can significantly reduce waste, as it typically requires less material compared to traditional welding methods.
Tips: Implement regular maintenance and calibration of equipment to ensure consistent results. Training personnel in the specific intricacies of thin film welding can also lead to improved efficiency and reduced error rates in production.
Thin film welding techniques are becoming increasingly pivotal in modern manufacturing, particularly in the electronics and medical device sectors. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global ultraSonic Welding market is projected to reach USD 8 billion by 2027, indicating a significant demand for advanced welding solutions. These techniques enable manufacturers to join materials with precision and minimal thermal impact, which is crucial for sensitive components.
Shenzhen Chengguan Intelligent Ultrasonic Equipment Co., Ltd. has been at the forefront of this innovation for over 20 years, specializing in ultrasonic Plastic Welding systems and equipment tailored for various industries. The company's expertise in ultrasonic technology facilitates the integration of thin film welding techniques, ensuring a reliable and efficient manufacturing process. As industries increasingly adopt automation and smart manufacturing practices, the demand for advanced ultrasonic welding solutions will continue to rise, making Chengguan’s offerings essential for achieving high quality and efficiency in production lines.
In modern manufacturing processes, thin film welding is gaining prominence as a superior alternative to traditional methods. Unlike conventional welding techniques that often require significant amounts of heat and energy, thin film welding utilizes lower temperatures, thereby reducing thermal distortion and enhancing material integrity. This method is particularly advantageous for delicate components or materials that are sensitive to heat, allowing for precision assembly and improved product quality.
Tips: When considering a shift to thin film welding, evaluate the specific materials and components being used. Testing different welding parameters can uncover the optimal settings for your application, leading to enhanced results and greater efficiency.
Moreover, traditional welding techniques often involve complex setups and longer cycles, which can hinder productivity. In contrast, thin film welding offers faster processing times and can be more easily automated, making it an attractive choice for high-volume manufacturing. This streamlined approach not only improves production rates but also lowers operating costs, providing manufacturers with a competitive edge in the market.
Tips: Keep in mind the importance of proper training for staff when implementing new welding technologies. Investing in employee education can lead to better utilization of thin film welding systems and result in higher quality outputs.
| Criteria | Thin Film Welding | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | High compatibility with various materials | Limited to certain materials |
| Heat Input | Low heat input, reducing thermal stress | High heat input, often leading to distortion |
| Speed of Process | Faster process time | Slower due to higher setup times |
| Precision | High precision in joining | Lower precision, more fusion defects |
| Cost Efficiency | More cost-effective in large-volume applications | Higher cost in material waste and defects |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible for various applications | Less flexible, specific to applications |
Thin film welding plays a critical role in modern manufacturing processes, particularly due to its ability to create strong, durable bonds in increasingly complex materials. However, implementing thin film welding is not without its challenges. One significant hurdle is the scalability of the technology; as manufacturers aim to produce larger quantities of products, maintaining consistent quality across batches becomes difficult. Variability in material properties and environmental conditions can lead to defects, requiring advanced quality control measures to ensure reliability in the final products.
Another challenge is the technical expertise required for effective implementation. Thin film welding involves intricate processes that demand a thorough understanding of material science and engineering principles. Manufacturers often find it difficult to recruit skilled personnel who can adeptly navigate the complexities of thin film technology. To overcome this, companies are investing in specialized training programs and collaborating with educational institutions to build a workforce capable of meeting the demands of modern production environments. Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on refining thin film welding techniques to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, making it more accessible to a wider range of industries.
The evolution of thin film welding is poised to significantly impact modern manufacturing processes, particularly with the increasing demand for lightweight materials in various industries. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the thin film technology market is projected to grow from $1.9 billion in 2022 to $3.4 billion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5%. This growth is driven by the rising need for high-performance materials in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where minimizing weight while maximizing strength is crucial.
Furthermore, advancements in laser and electron beam welding techniques are enhancing the efficiency and precision of thin film welding. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology highlights that the integration of automation and artificial intelligence in welding processes is expected to reduce production times by up to 30% and improve joint quality. As manufacturers increasingly adopt these technologies, they position themselves to meet the rigorous standards set by eco-friendly initiatives and customer expectations for innovative products. The future of thin film welding not only looks promising but is also a critical factor in the sustainability journey of modern manufacturing.
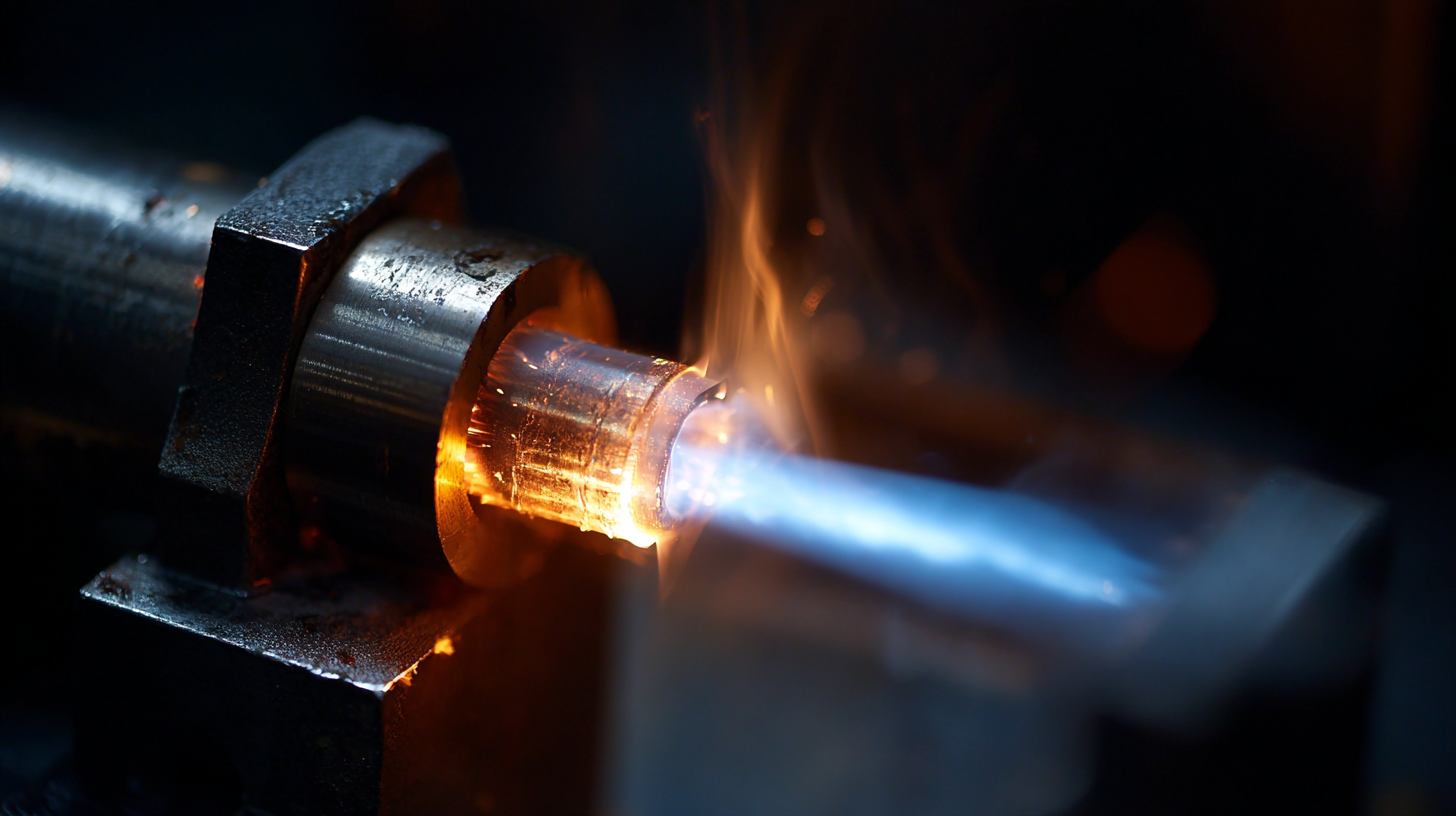

Thin film welding technologies play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of modern manufacturing processes. By utilizing advanced techniques such as laser welding and electron beam welding, manufacturers can significantly decrease material waste and energy consumption.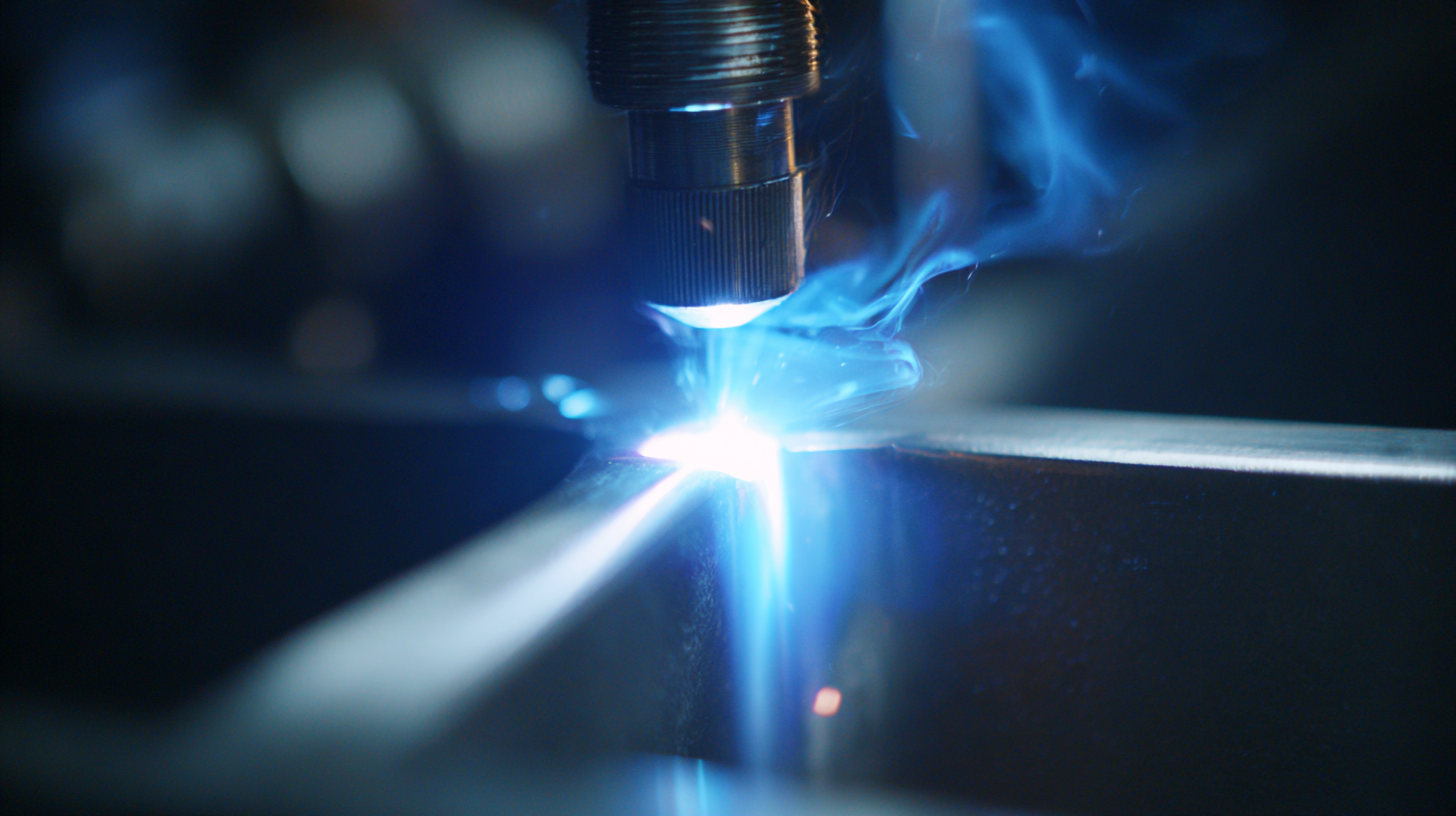  These methods enable precise joining of materials at lower temperatures, which not only conserves energy but also minimizes the thermal degradation of components. As a result, products require less raw material input and have a longer lifecycle, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
These methods enable precise joining of materials at lower temperatures, which not only conserves energy but also minimizes the thermal degradation of components. As a result, products require less raw material input and have a longer lifecycle, contributing to more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Furthermore, thin film welding supports the development of lightweight and efficient products, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace. Lighter products lead to lower fuel consumption during operation, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the reduced need for bulky and heavy components allows for innovative designs that can further enhance performance and sustainability.
Overall, the adoption of thin film welding technologies aligns with the industry's goals of minimizing its ecological footprint while maintaining high-quality production standards.
The CGTC Series Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Machine represents cutting-edge technology in the realm of ultrasonic welding, leveraging a combination of design and material advancements for superior performance. With a thickened steel body and a concentric straight axis design, this machine exhibits enhanced structural stability, ensuring precise and consistent welding outcomes. According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the ultrasonic welding equipment market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing demand for automated production processes in sectors like automotive and electronics, where precision is paramount.
The upgraded titanium alloy through-rod transducer featured in the CGTC series is fully compatible with various mold materials, including steel, aluminum, and titanium, expanding its usability across diverse applications. This versatility is complemented by the machine's horizontal four-point adjustment system, which simplifies mold modifications and enhances operational efficiency. As noted in a recent technical analysis, the ability to adapt rapidly to different production needs without compromising on quality is a key factor in the adoption of advanced welding technologies.
Moreover, the CGTC Series is equipped with a capacitance digital matching system, ensuring that the ceramic tiles used are fully compatible with the machine's operational framework. This innovative operating system supports 485 communication and digital operation, facilitating seamless integration into modern manufacturing systems. Industry analysts predict that manufacturers adopting such high-tech ultrasonic welding machines will see a marked improvement in production speed and cost-effectiveness, further underscoring the CGTC series' role in shaping the future of welding technology.
: Thin film welding is a technique that facilitates precise control over the welding process, enhancing production efficiency and product quality. It is particularly important in industries like electronics and aerospace, where strong, reliable bonds are essential.
Thin film welding significantly reduces material waste compared to traditional welding methods, as it typically requires less material to achieve strong bonds between components.
Thin film welding techniques, such as laser and electron beam welding, decrease energy consumption and material waste, leading to more sustainable manufacturing practices and longer product lifecycles.
Thin film welding is versatile and can be employed across a variety of materials, including metals, polymers, and ceramics, suitable for various advanced manufacturing applications.
To optimize the process, maintain optimal temperature control to prevent material degradation, and consider pre-treating surfaces to enhance adhesion quality.
By enabling precise joining at lower temperatures and reducing the need for raw materials, thin film welding contributes to products having a longer lifecycle and a reduced ecological footprint.
Training personnel on the specific intricacies of thin film welding can lead to improved efficiency and reduced error rates during production.
Lightweight products result in lower fuel consumption during operation, leading to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, which enhances overall sustainability.
Regular maintenance and calibration of equipment are essential to ensure consistent results and high-quality production in thin film welding processes.
Thin Film Welding is increasingly recognized as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing processes, providing significant advantages over traditional welding methods. Its key benefits include enhanced precision, reduced material waste, and the ability to join dissimilar materials, making it an essential technique in various advanced manufacturing sectors. Innovative applications range from electronics to automotive industries, showcasing its versatility and efficiency.
However, the implementation of Thin Film Welding is not without challenges, such as the need for specialized equipment and potential quality control issues. Companies like Shenzhen Chengguan Intelligent Ultrasonic Equipment Co., Ltd. are at the forefront, providing cutting-edge ultrasonic welding systems that integrate Thin Film Welding techniques, addressing these challenges while promoting sustainability. As the industry evolves, the integration of Thin Film Welding is expected to grow, significantly impacting manufacturing landscapes and environmental outcomes.