

In today’s fast-changing tech world, 'Thin Film Welding' is really gaining importance across a bunch of different industries — from electronics to renewable energy setups. Experts like Dr. Emily Johnson, who's a top researcher at the Institute of Advanced Manufacturing, keep stressing how crucial it is to develop reliable welding methods. She often says, “The key to successful thin film tech is mastering welding techniques that give us perfect adhesion and performance.” As more industries turn to thin films because of their lightness and versatility, it’s become super important to know how to weld these fragile materials properly.
Getting thin film welding right isn’t just about making the parts last longer — it also boosts the overall efficiency of the devices we're working on. When done well, it helps engineers create films that can handle tough conditions, which means better quality and more dependable products. In this overview, we’ll take a look at some key thin film welding practices that professionals should really get familiar with if they want to see great results and keep pushing technology forward. By checking out what industry experts have to say, we hope to give practitioners the know-how they need to really excel in the world of Thin Film Welding.
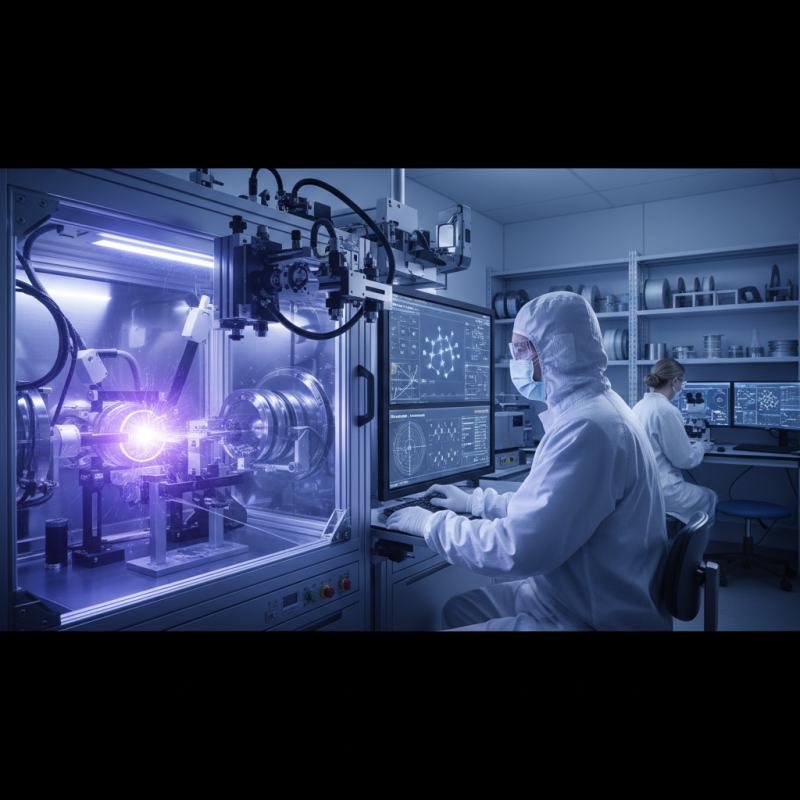

Thin film welding is a precise technique utilized to join materials at a microscale, often employed in industries such as electronics, solar energy, and biomedical devices. At its core, this method involves the application of heat or pressure to fuse thin layers of materials together, resulting in a strong, durable bond. Understanding the fundamentals of thin film welding is essential for engineers and technicians who aim to enhance the reliability and performance of their products. The process requires careful consideration of factors such as material compatibility, heating rates, and the ambient environment, all of which can significantly impact the quality of the weld.
In addition to the technical aspects, it's crucial to comprehend the specific applications of thin film welding. This technique is particularly advantageous in scenarios where traditional welding methods might compromise the integrity of fragile materials. For instance, thin film welding enables the assembly of lightweight components without the added weight of fasteners, making it a preferred choice in aerospace and automotive industries. By mastering the principles of thin film welding, professionals can innovate new designs and improve the manufacturing processes, leading to advanced material solutions and superior product performance.
Thin film welding techniques are becoming increasingly essential across various industries, including electronics, aerospace, and renewable energy. The effectiveness of these techniques largely depends on the selection of appropriate materials. Commonly used materials in thin film welding include metals such as titanium, aluminum, and nickel, which are favored for their excellent thermal conductivity and strength-to-weight ratios. According to a report by the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, the use of titanium in thin film applications has increased by 25% over the past five years due to its corrosion resistance and high fatigue strength.
Additionally, polymers such as polyethylene and polyimide are also integral in thin film welding, particularly in the electronics sector, where flexibility and thermal stability are crucial. Research from the Journal of Polymer Science indicates that the demand for polymer-based thin films has surged by over 30% in recent years, driven by the rising need for lightweight and high-performance materials in devices such as smartphones and solar panels. These materials must be carefully chosen based on specific welding techniques, as their properties directly influence joint strength and durability. Understanding these key materials can significantly impact the success of thin film welding projects and contribute to advancements in technology.
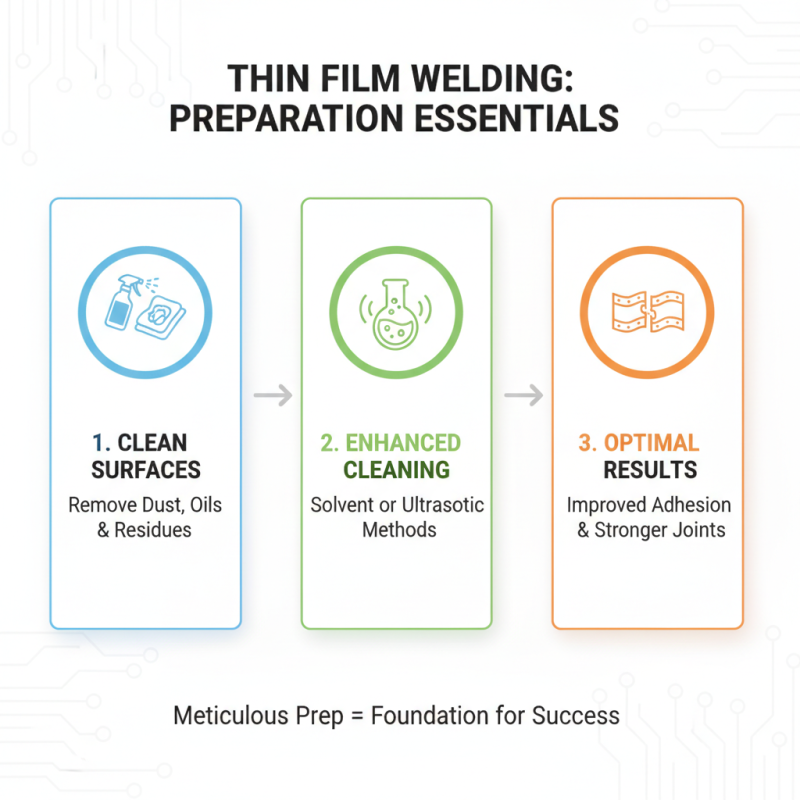
When it comes to effective thin film welding, meticulous preparation is essential for achieving optimal results. The first step involves ensuring that the surfaces to be welded are clean and free from contaminants. Any residues such as dust, oils, or previous coatings can impair adhesion and weaken the joint. Utilizing solvent cleaning or ultrasonic cleaning methods can significantly enhance surface cleanliness, setting a solid foundation for the welding process.
Next, proper surface treatment is vital. Depending on the materials being welded, techniques such as plasma treatment or chemical etching can be employed to increase surface energy and promote better bonding. Additionally, precise alignment of the components is crucial. Utilizing jigs or fixtures can ensure consistent spacing and orientation, preventing issues that could arise during the welding process. By carefully following these preparation steps, welders can significantly improve the quality and durability of their thin film joints.
Thin film welding techniques are essential in various industries, including electronics, aerospace, and renewable energy. The most common methods include vapor deposition, laser welding, and ultraSonic Welding, each tailored to specific applications. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global thin film technology market is projected to reach USD 35.54 billion by 2026, indicating a growing demand for these advanced techniques.
Vapor deposition techniques, such as Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), are frequently used for creating high-quality thin films on substrates. These methods are particularly effective in the semiconductor and photovoltaic sectors. For instance, PVD processes can achieve films as thin as a few nanometers, which is critical for manufacturing smaller and more efficient electronic components. Meanwhile, laser welding provides precision and control in joining thin materials without affecting the overall structure, making it ideal for medical devices and complex machinery.
Ultrasonic welding is another prevalent technique, especially in the automotive and textile industries. This method utilizes high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to generate localized heat, effectively fusing thermoplastic materials. Reports indicate that ultrasonic welding is gaining traction due to its efficiency and ability to produce strong, reliable joints without the need for adhesives. As the demand for lightweight and durable materials continues to rise, understanding these common thin film welding techniques and their applications will be crucial for engineers and manufacturers alike.

In the realm of thin film welding, quality control measures play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and performance of welded assemblies. According to a recent report by Industry Insights, nearly 35% of failures in thin film applications can be traced back to inadequate quality control during the welding process. Implementing stringent monitoring protocols can mitigate these risks significantly. For instance, conducting regular inspections of weld seams and utilizing automated imaging systems can enhance the detection of flaws, resulting in a more reliable final product.
Tips for effective quality control include establishing a standardized procedure for thermal analysis of the weld zones. This helps in identifying inconsistencies in temperature distribution, which can severely impact the mechanical properties of the welded material. Additionally, maintaining a controlled environment during the welding process, such as minimizing contamination and ensuring optimal temperature, is vital. A study by the Welding Institute suggests that environmental factors can influence up to 50% of welding outcomes, emphasizing the need for precision in the fabrication setting.
Another essential aspect of quality control is the training and certification of personnel involved in the welding process. Data indicates that organizations with well-trained staff report up to 60% fewer defects than those with less experienced operators. Regularly updating training programs to incorporate the latest technologies and methods can lead to substantial improvements in welding quality. Engaging in these practices will not only enhance the overall quality of thin film welds but also ensure compliance with industry standards.
Troubleshooting common issues in thin film welding is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and quality of welded components. One of the frequent problems encountered is inadequate adhesion between film layers. This can be attributed to surface contamination or improper surface preparation before welding. To mitigate this, it's essential to maintain clean work surfaces, utilizing compatible solvents or cleaning agents to remove any residues effectively. Additionally, adjusting the welding parameters, such as temperature and pressure, can enhance adhesion by promoting better interlayer fusion.
Another common issue is the occurrence of bubbles or voids within the weld. These imperfections can compromise the integrity of the final product. Bubbles often arise from entrapped air or volatiles during the welding process. To address this, consider pre-heating the materials to allow for better out-gassing and provide ample time for the film to settle before cooling. Furthermore, utilizing controlled environments, such as vacuum chambers, can significantly reduce the likelihood of bubble formation, leading to improved weld quality.
Finally, variations in thickness across the weld seam can contribute to mechanical failures. Ensuring uniform pressure distribution during the welding process is essential. Employing fixtures that hold the thin films securely in place can prevent movement that could lead to inconsistencies. Regularly inspecting equipment and implementing consistent procedures can also help maintain uniformity, thus enhancing the overall reliability of thin film welding operations.
The future of thin film welding technologies is poised for significant advancements driven by the increasing demand for efficiency, precision, and sustainability in manufacturing processes. Emerging techniques are harnessing the power of automation and artificial intelligence to enhance the quality and speed of welding operations. As industries continue to integrate smart manufacturing practices, the role of machine learning algorithms in monitoring and optimizing welding parameters will become paramount, allowing for real-time adjustments that improve the overall integrity of the welded films.
Moreover, the exploration of advanced materials is set to redefine thin film welding by enabling the use of lighter and more resilient films that can withstand extreme conditions. Innovations such as laser welding and ultrasonic welding are gaining traction, offering superior bonding mechanisms while minimizing thermal deformation. As sustainability becomes a key focus, research into eco-friendly welding processes that reduce energy consumption and minimize waste will likely shape the direction of future developments in thin film welding. Ultimately, these trends will not only enhance the efficiency of production lines but also align with the growing emphasis on environmentally responsible manufacturing practices.
The latest market analysis highlights significant advancements in ultrasonic Plastic Welding technology, particularly emphasizing the benefits of the CGTC Series Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Machine. Its thickened steel body combined with a concentric straight axis design enhances structural stability and precision during the welding process. This robust construction not only supports accurate welds but also contributes to a longer service life for the machine, making it an excellent investment for manufacturers focused on efficiency.
An essential feature of this ultrasonic welding machine is its upgraded titanium alloy through-rod transducer, which is fully compatible with a range of materials including steel, aluminum, and titanium molds. This versatility allows for seamless transitions between different welding applications, accommodating various industrial needs. Additionally, the machine offers horizontal four-point adjustment, facilitating convenient mold adjustments that enhance usability in diverse application scenarios.
Furthermore, the innovative capacitance digital matching system improves operational efficiency by ensuring that the digital components interact flawlessly with the machine's physical elements. Coupled with a new operating system that supports 485 communication and facilitates digital operation, users can expect a machine that not only meets but exceeds the standards of modern plastic welding requirements. This technology positions the CGTC Series as a formidable solution for enhancing productivity and quality in plastic welding processes.
: Thin film welding is a precise technique used to join materials at a microscale, applying heat or pressure to fuse thin layers together, creating strong and durable bonds.
This technique is beneficial in scenarios where traditional welding might damage fragile materials, allowing for the assembly of lightweight components without the use of additional fasteners.
Common materials include metals such as titanium, aluminum, and nickel, as well as polymers like polyethylene and polyimide, selected for their favorable properties such as thermal conductivity and flexibility.
The chosen materials significantly influence joint strength and durability; therefore, appropriate material selection based on specific welding techniques is critical for the success of thin film welding projects.
Quality control is crucial for ensuring the integrity and performance of welded assemblies, as inadequate quality control can lead to a significant percentage of failures in thin film applications.
Implementing stringent monitoring protocols, conducting regular inspections, maintaining a controlled environment, and establishing a standardized procedure for thermal analysis are effective quality control measures.
Organizations with well-trained personnel experience significantly fewer defects, as ongoing training and certification ensure staff are knowledgeable about the latest technologies and methods.
Environmental factors, including contamination and temperature control, can have a substantial impact on the welding outcomes, indicating the necessity for precision in the fabrication setting.
Regular inspections enhance the detection of flaws, which is fundamental to achieving a more reliable final product in thin film welding applications.
There has been an increasing demand for materials such as titanium and polymer-based thin films due to their desirable properties and applications in lightweight and high-performance technological devices.
Thin Film Welding is an advanced technique used in various industries for joining materials with high precision. The article provides a comprehensive overview of Thin Film Welding, beginning with its fundamental principles and the key materials involved in the process. Fundamental preparation steps are essential to ensure effective bonding, and various common techniques, such as laser and ultrasonic welding, highlight its diverse applications across sectors.
In addition to discussing the importance of quality control measures to maintain high standards in Thin Film Welding processes, the article addresses troubleshooting common issues that can arise during welding. Finally, it looks at future trends in Thin Film Welding technologies, indicating ongoing advancements that promise to enhance efficiency and broaden applications, making it a vital area of focus for researchers and industry professionals alike.








