

When it comes to creating strong and lasting joints in metal fabrication, getting the hang of different welding techniques is really important. The quality of your welds has a huge impact on how sturdy and long-lasting your structures will be, so it’s pretty much a must for engineers and fabricators to know the best practices. In this article, I’ll walk you through the top five welding methods that not only make your joints more reliable but also help speed up your projects.
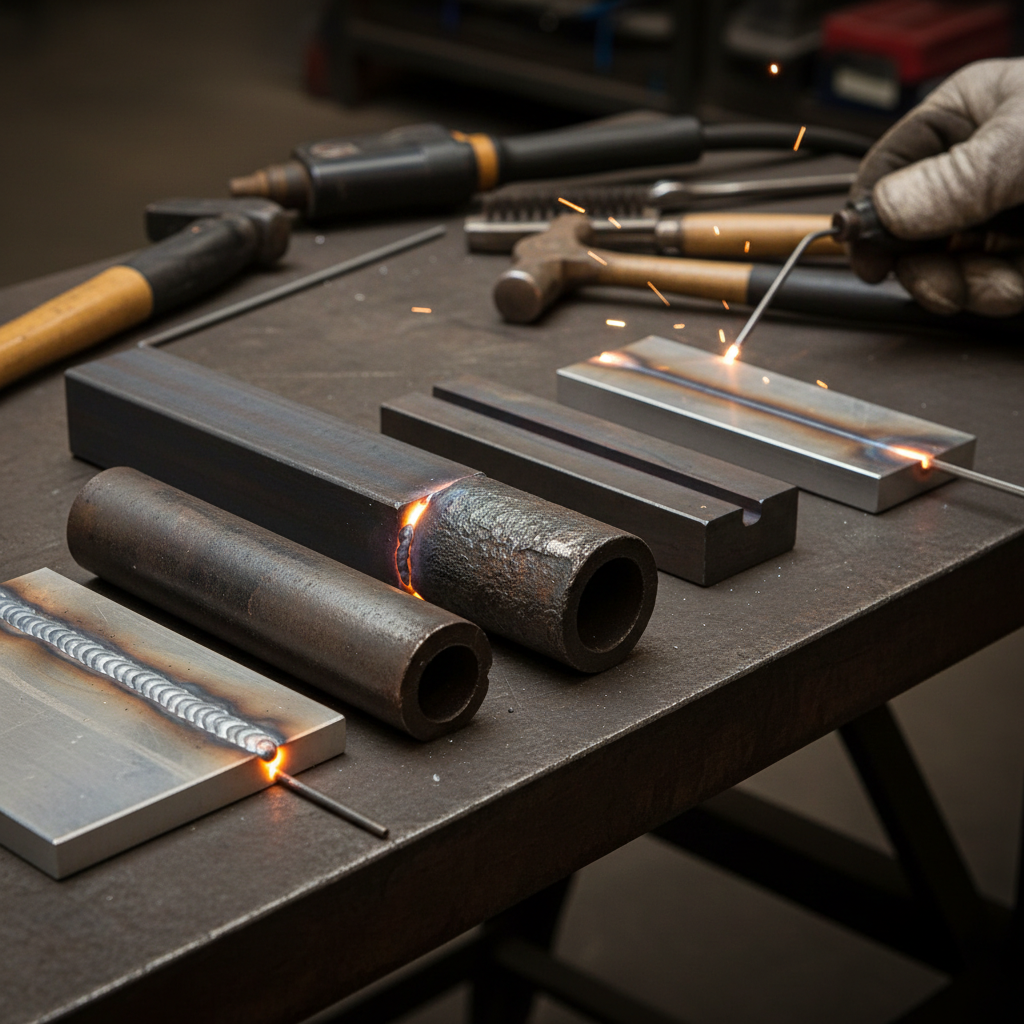

Whether it’s MIG, TIG, stick welding, or something else, each technique has its own perks suited for different kinds of materials and situations. By understanding what makes each method special and when to use them, you can make smarter choices that lead to better results.
Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, the tips I’ll share will help boost your welding game and make sure your seams are solid every time. So, let’s dive into these must-know welding techniques and set you up for success in all your future projects.
When it comes to achieving optimal joint strength in Metal Welding, understanding essential techniques is crucial for any welder. According to the American Welding Society, improper welding can lead to joint failure, with more than 50% of manufacturing defects attributed to inadequate weld quality. Therefore, mastering various welding methods not only enhances the durability of your projects but also ensures safety and reliability.
One noteworthy technique is MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, which uses a continuous wire feed and a shielding gas to protect the weld pool. This method is favored for its speed and versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. However, ensuring proper heat settings and travel speeds can significantly impact the strength of the joint.
**Tips:** Always perform a thorough inspection of your materials before welding. Look for contaminants such as rust or grease that can compromise weld quality. Additionally, maintaining a consistent travel speed can help achieve uniform penetration and reduce the likelihood of defects.
Another critical approach is TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, renowned for its precision. Utilizing a non-consumable tungsten electrode, TIG welding provides greater control over the weld pool, leading to stronger and cleaner joints. However, it typically requires more skill and diligence, making training and practice essential for success.
**Tips:** To enhance your TIG welding skills, practice on scrap materials before working on critical components. Utilize different electrode materials and filler metals to understand their properties and how they affect joint strength in various applications.
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are two prominent techniques known for their unique advantages in metal fabrication. MIG welding is celebrated for its speed and ease of use. It utilizes a continuous wire feed as an electrode, which melts to form the weld pool. This method is particularly effective for thicker materials and is favored in industrial applications due to its high productivity. The simplicity of MIG welding also makes it accessible for beginners, allowing for faster learning and execution in various welding projects.
On the other hand, TIG welding is renowned for its precision and control. This technique uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce a high-quality weld, allowing welders to apply the filler material manually. The versatility of TIG welding makes it suitable for thinner materials and intricate designs, often required in applications like aerospace and automotive industries. While it demands more skill and time compared to MIG welding, the results are remarkable, yielding strong, clean, and aesthetically pleasing joints. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right technique for your specific welding needs.
| Welding Technique | Best For | Pros | Cons | Material Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIG Welding | Thin to medium materials | Fast, easy to learn | Less control in weld quality | Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel |
| TIG Welding | Thin materials, precision work | High quality, versatile | Slower process, requires skill | Steel, Aluminum, Copper, Titanium |
| Stick Welding | Outdoor use, thick materials | Powerful, portable | Less clean finish | Steel, Cast Iron |
| Flux-Cored Arc Welding | Thick materials, outdoor structures | Good penetration | Requires a shielding gas | Steel, Stainless Steel |
| Submerged Arc Welding | Thick steel fabrication | High deposition rate | Expensive equipment | Steel, Stainless Steel |
| Electroslag Welding | Heavy plate components | Very high efficiency | Requires skill, limited to thick plates | Thick steel sections |
| Plasma Arc Welding | Thin metals, precise work | High precision | Complex setup | Steel, Aluminum, Copper |
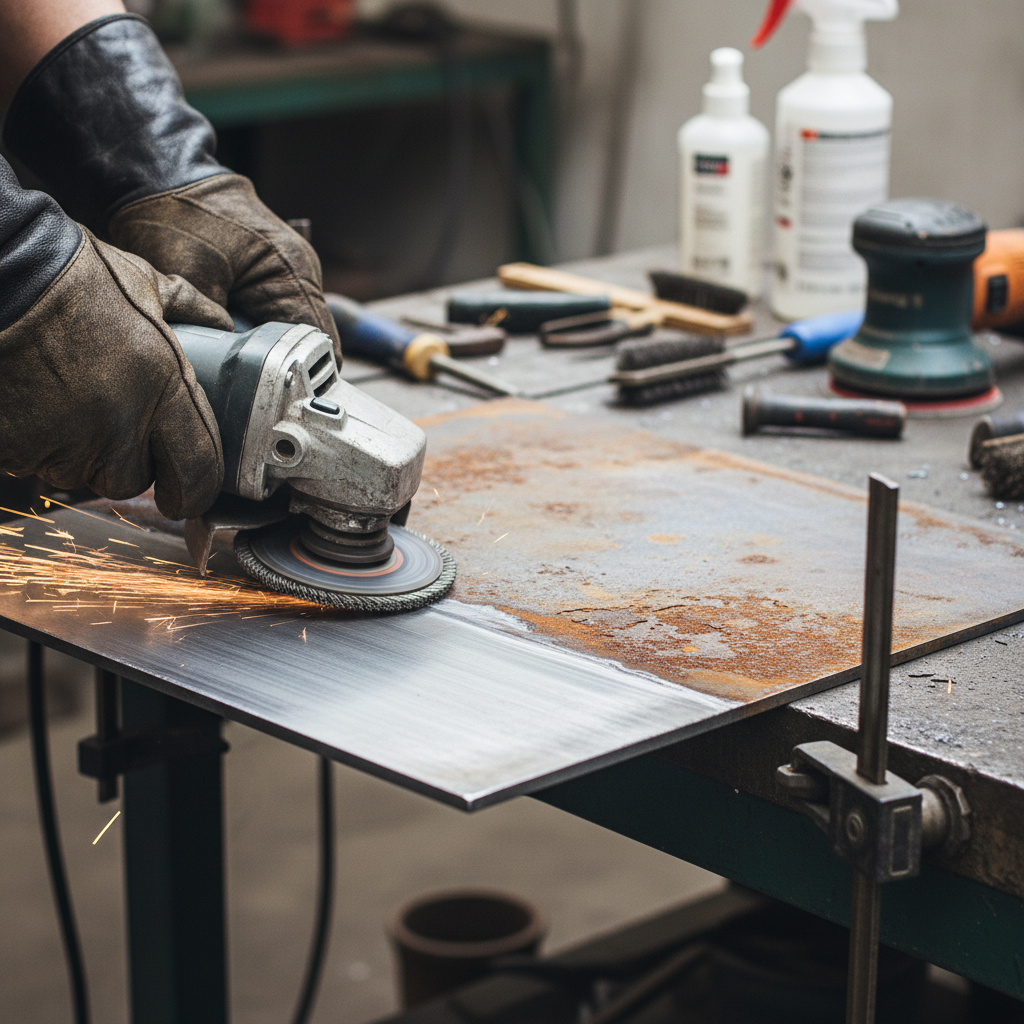

Preparing metal surfaces before welding is crucial for achieving strong and durable joints. The first step in this process is to thoroughly clean the surfaces to remove any contaminants such as dust, oil, and rust. Using a wire brush, grinder, or chemical cleaner can effectively prepare the metal for welding. This ensures that the weld can penetrate the base metal properly, leading to better adhesion and overall strength in the finished joint.
In addition to cleaning, it is important to ensure proper fit-up between the pieces being welded. Gaps and misalignments can result in weak points in the weld, making the joint susceptible to failure. Using jigs or clamps can help maintain the correct positioning during the welding process. Finally, beveling the edges of thicker materials can facilitate better penetration and fusion during welding, resulting in a stronger joint. By adhering to these best practices in surface preparation, welders can significantly enhance the quality and durability of their welds.
Effective heat management is crucial in welding processes to prevent warping and distortion, which can compromise the strength and durability of the joints. According to a report by the American Welding Society, nearly 70% of welders reported that heat-related issues, such as warping, were the leading cause of rework in their projects. To mitigate these effects, controlling the heat input and utilizing proper welding techniques is essential.
One key tip is to employ preheating methods tailored for specific metals. For example, materials like high-carbon steel require preheating to minimize stress during the cooling phase. Additionally, interpass temperature control should be maintained to ensure uniform cooling. This is vital for materials such as aluminum and stainless steel, where rapid cooling can lead to cracking. Another effective strategy is to use stitch welding techniques, which allow for reduced heat concentration and promote even thermal distribution across the weld bead.
Lastly, consider the use of advanced Welding Equipment that offers better control over the heat input. Tools that incorporate pulsed welding technology can help in managing the temperature, thereby reducing thermal distortion. As a result, not only will this lead to stronger joints, but it will also decrease the likelihood of costly rework, promoting overall efficiency in the welding process.
When it comes to enhancing the durability of welded joints, the choice of filler material is crucial. Selecting the right filler not only influences the mechanical properties of the weld but also its resistance to environmental factors such as corrosion and temperature fluctuations. According to a report by the American Welding Society, nearly 50% of workplace failures in metallic structures are attributed to inadequate filler choices, highlighting the significance of this decision in the welding process.
Different applications require different filler materials, with options ranging from stainless steel to aluminum alloys. For instance, using a nickel-based filler material can significantly improve the toughness and corrosion resistance of the weld, making it ideal for applications in chemical processing industries. Data from the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology shows that the use of high-performance welding fillers can increase the overall lifespan of a welded joint by up to 30%, underscoring the importance of tailoring filler material selection based on environmental and structural demands. By understanding the implications of filler materials and choosing wisely, welders can ensure stronger and more durable joints.
Post-weld treatment plays a crucial role in enhancing the integrity of welded joints, ensuring they stand the test of time and stress. Proper techniques after welding can help mitigate any residual stresses and improve the mechanical properties of the weld. One popular method is stress relieving, which involves heating the welded joints to a specific temperature and then cooling them slowly. This process helps to alleviate internal stresses and reduce the risk of cracking.
Another effective technique is shot peening, which involves bombarding the surface of the weld with small metal beads. This method induces residual compressive stresses, increasing fatigue resistance and extending the joint's lifespan. Applying a protective coating can also be beneficial as it guards against corrosion, especially in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals.
**Tips:** When performing post-weld treatments, always ensure the temperature is monitored accurately to prevent overheating. Implementing a systematic cleaning procedure before any treatment can also improve the effectiveness of subsequent protective measures. Lastly, consider the specific demands of your project, as different materials may require tailored post-weld techniques for optimal results.
The landscape of metal welding machines, particularly for copper wire applications, is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and increasing market demand. One of the standout innovations is low-temperature welding, which eliminates the need for high-temperature metal melting. This process not only protects the properties of base materials but also mitigates risks associated with deformation and brittleness often triggered by extreme heat. As industries push for solutions that preserve material integrity, low-temperature welding presents an attractive option for manufacturers.
Moreover, environmental sustainability is becoming a pivotal aspect of welding processes. Modern metal welding machines are designed to operate without flux or filler materials, resulting in cleaner operations that adhere to strict environmental standards. By eliminating harmful gases and slag, these machines significantly reduce post-welding cleaning requirements, enhancing operational efficiency. High welding quality is another critical advantage, with welded joints achieving exceptional strength and sealing capabilities. This makes such machines particularly suitable for industries where precise welding quality is non-negotiable, including electronics and aerospace.
Additionally, the robust adaptability of these machines allows them to accommodate a diverse range of metal materials. They can seamlessly handle similar or dissimilar metals, such as copper-aluminum or nickel-stainless steel combinations, expanding their applicability across various sectors. As industries increasingly demand versatile and efficient welding solutions, advancements in metal welding technology continue to shape market dynamics, highlighting the importance of investing in machines that not only meet current needs but also anticipate future challenges.
: MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding uses a continuous wire feed and shielding gas to protect the weld pool. It is favored for its speed and versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Always inspect your materials for contaminants like rust or grease before welding. Additionally, maintaining a consistent travel speed can help ensure uniform penetration and reduce defects.
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is known for its precision, utilizing a non-consumable tungsten electrode. It provides greater control over the weld pool, leading to stronger and cleaner joints, but requires more skill than MIG welding.
The right filler material influences the mechanical properties of the weld and its resistance to environmental factors. Nearly 50% of workplace failures in metallic structures are attributed to inadequate filler choices.
Using high-performance welding fillers can increase the overall lifespan of a welded joint by up to 30%, emphasizing the necessity of selecting the appropriate fillers based on specific environmental and structural demands.
Effective techniques include stress relieving, which involves heating the welded joints to a specific temperature and cooling them slowly, and shot peening, which bombards the weld surface with small metal beads to increase fatigue resistance.
Accurate temperature monitoring is crucial to prevent overheating, which can compromise the integrity of the weld during post-weld treatments.
Protective coatings guard against corrosion, particularly in environments that are exposed to moisture or chemicals, enhancing the longevity and integrity of the welded joints.
The specific demands of your project should be considered, as different materials may require tailored post-weld techniques for optimal results.
Welders can enhance their TIG welding skills by practicing on scrap materials and experimenting with different electrode materials and filler metals to understand their properties and effects on joint strength.
This article highlights essential metal weld techniques that are crucial for achieving stronger and more durable joints. It discusses the differences between MIG and TIG welding, both of which play significant roles in various metal fabrication projects. The importance of properly preparing metal surfaces before welding is emphasized to ensure optimal joint strength, along with effective heat management to prevent warping and distortion in welds. Selecting the right filler material is another key factor that enhances the durability of the welds. Additionally, post-weld treatment techniques are explored, which can significantly improve joint integrity and long-term performance.
At Shenzhen Chengguan Intelligent Ultrasonic Equipment Co., Ltd., we understand the significance of quality in metal weld processes, as our expertise in ultraSonic Welding systems has allowed us to serve various industries for over 20 years. By integrating advanced welding techniques with our ultrasonic technology, we aim to provide solutions that ensure robust and resilient metal connections, meeting the diverse needs of our clients in the manufacturing sector.








