

You know, Non-Woven Fabric Welding is pretty important across a bunch of industries, especially in things like automotive and textiles. I read somewhere that, according to MarketsandMarkets, the non-woven fabric market is set to hit around $50 billion by 2025. That’s crazy! This really shows how much the need for better, faster fabric bonding methods is growing. Big players like DuPont and Freudenberg are really pushing the envelope here, making a big difference in how efficiently products get made.
When it comes to welding non-woven fabrics, there are quite a few options, and not all of them are equally effective. For example, hot air welding is pretty popular because it’s quick and versatile — you can use it in a bunch of different situations. On the other hand, Ultrasonic Welding offers super precise joints and is really strong. Still, even with all these tech jumps, there are challenges. For instance, getting consistent quality can be tricky, especially for manufacturers still figuring out the ropes with new techniques.
As non-woven fabrics become more popular, that brings both new opportunities and some hurdles to jump over. The industry’s always changing, so we’ve gotta keep developing better ways to bond these materials. Ongoing research is crucial — things like adapting to different material types and thicknesses. If manufacturers want to stay competitive, they really need to stay on top of these tech advances and keep tweaking their processes. Ultimately, tackling these challenges head-on is key if they want to succeed in the fast-paced world of non-woven fabric welding.
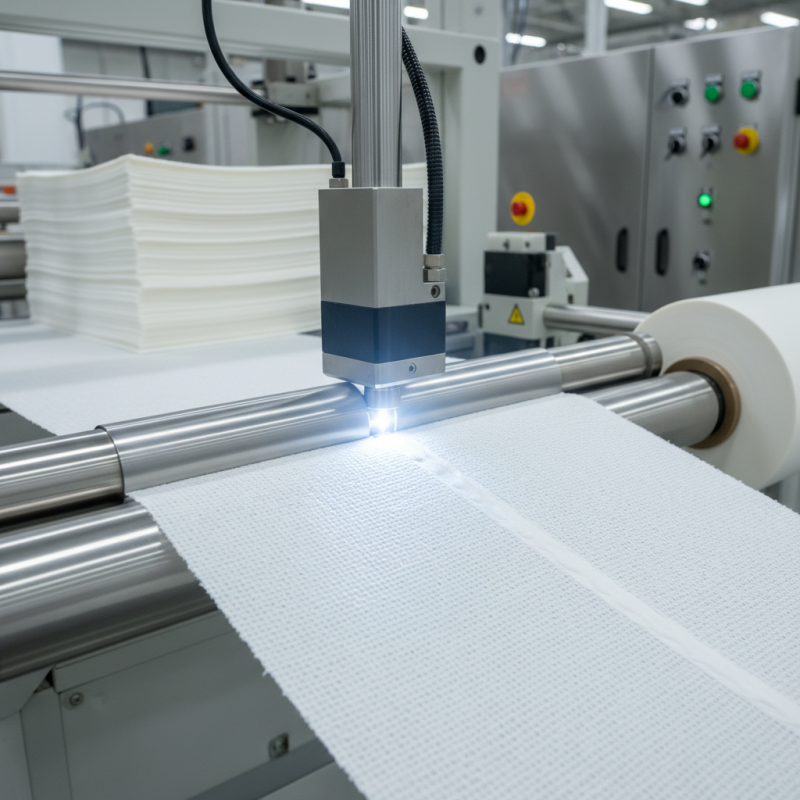

Non-woven fabrics are widely used due to their versatility. Welding techniques play a key role in their production and application. Understanding the top five welding methods can enhance your project outcomes significantly.
Ultrasonic welding utilizes high-frequency sound waves. This method is quick and efficient. It creates strong seams without additional materials. However, it requires precise equipment. Misalignment can lead to weak joints.
Hot air welding is another popular method. It combines heat and pressure, resulting in strong bonds. Yet, controlling the temperature is crucial. Overheating can damage the fabric.
Laser welding is innovative and precise. It allows for intricate designs and strong connections. However, the technology can be expensive.
Mechanical welding methods involve stitching or sealing. They are often more accessible but less durable. Each method has its pros and cons. Selecting the right technique depends on your specific needs and resources.
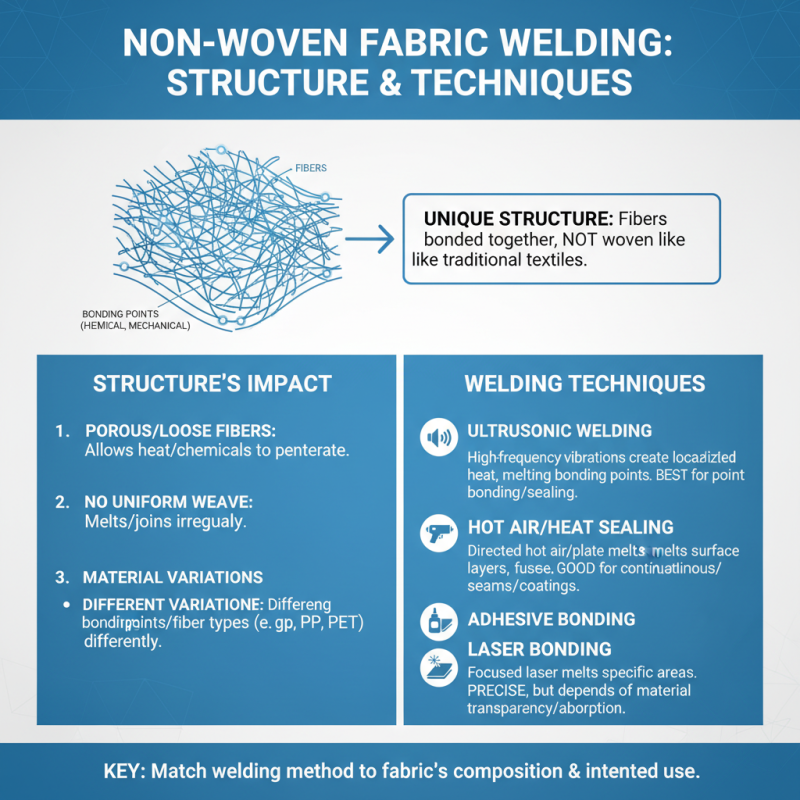
Non-woven fabrics have gained popularity for their versatility and functionality. Understanding their structure is crucial for effective welding techniques. These fabrics are made from fibers bonded together, often through heat, chemicals, or mechanical means. This unique composition affects how different welding methods work.
Welding non-woven fabrics can be tricky. The fusion of fibers needs precision. Too much heat can damage the material, while too little will fail to bond. Testing various settings is crucial. Each fabric behaves differently. You may find some welds appearing strong but ultimately failing under stress. It’s all about finding the right balance.
Tips: Always start with small samples. Experiment with heat settings. Adjust your speed when welding. This will save resources and help you understand the fabric better. Another tip is to keep surfaces clean. Dirt can lead to weak welds. Lastly, document your findings. What works on one type may not work on another. Learning from each trial is key.
Thermal welding is a popular method for joining non-woven fabrics. This process uses heat to melt the fabric edges and fuse them together. It’s efficient and creates strong bonds. The equipment is relatively simple, yet effective. However, controlling temperature is critical. Too much heat can damage the fabric.
The science behind thermal welding lies in the melting point of materials. Non-woven fabrics consist of synthetic fibers, making them suitable for this method. The parameters must be precisely set. Timing, temperature, and pressure all play vital roles. Miscalculating these can lead to weak seams. It's a balance between efficiency and quality.
Applications of thermal welding are vast. It is widely used in medical, automotive, and packaging sectors. Each industry has unique requirements. The challenges can be different too. For instance, some materials might not weld easily. Finding the right settings often requires experimentation. As industries evolve, so does the need for refined techniques. Understanding the science helps improve results.
Ultrasonic welding has revolutionized the non-woven fabric industry. This method offers high efficiency and significant benefits. It employs high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to bond materials. The process is fast, with an average cycle time of under one second. This speed enhances productivity, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Recent industry reports indicate that ultrasonic welding can achieve bond strengths exceeding 90% of the parent material's strength. This is crucial in applications like hygiene products and medical supplies. Additionally, it minimizes the use of adhesives and eliminates the need for additional materials. Such savings contribute to greener manufacturing processes.
However, the technology is not without its challenges. Precise control over frequency and amplitude is essential for optimal results. Inconsistent parameters can lead to weak welds. Manufacturers must invest in proper training and equipment to ensure reliability. While ultrasonic welding is effective, ongoing refinement and understanding of its limitations are necessary for consistent quality.

Hot Air Welding is a crucial method in non-woven fabric applications. This technique uses a stream of heated air to bond fabric layers together. It's widely employed in industries like automotive, medical, and textile manufacturing. According to a recent industry report, over 35% of textile applications utilize hot air welding due to its efficiency and effectiveness.
During the hot air welding process, controlling the temperature is vital. If the heat is too high, it could damage the material. Conversely, if the heat is too low, the bond may not be strong enough. This delicate balance is essential to achieve seam integrity. Research indicates that a temperature difference of just a few degrees can significantly impact the joint strength.
Moreover, the equipment used in hot air welding must be regularly maintained. Neglecting this can lead to inconsistent results. Operators often encounter challenges in achieving uniformity in seam appearance and strength. Despite advancements in technology, managing these variables continues to be a topic for discussion among professionals. Continuous training in this area is necessary for ensuring product quality.
Laser welding has emerged as a preferred method for joining non-woven fabrics, thanks to its precision and versatility. This technology utilizes focused laser beams that can melt and fuse materials together. According to a report by Research and Markets, the laser welding market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by increasing applications across various industries, including textiles.
One main advantage of laser welding is its adaptability. It can work on different types of non-woven fabrics, providing a strong bond without compromising the fabric's integrity. For example, it’s effective for merging layers in medical textiles where cleanliness and strength are crucial. However, precision can be a double-edged sword. If settings are not calibrated correctly, the fabric can burn or weaken, leading to waste and potential customer dissatisfaction.
Moreover, the energy consumption in laser welding can be a concern. While it’s efficient, high power can lead to overheating and degradation of the materials. It's essential for manufacturers to monitor energy levels closely. The technology also requires skilled operators who understand the nuances of the laser system. A lack of expertise can result in inconsistent welding quality, reflecting the need for ongoing training.
When comparing non-woven fabric welding methods, strength and durability are critical metrics. Hot air welding is known for creating strong seams. It relies on heated air to bond fabrics together. However, it may not always provide the best visual appeal. In some cases, seams can appear uneven or lumpy.
Ultrasonic welding stands out for its precision. It uses high-frequency sound waves to melt fabric edges together. This method offers clean seams, improving overall aesthetics. But, the process can be costly. Additionally, not all fabrics are suitable for ultrasonic welding, limiting its versatility.
Laser welding is another method that provides impressive results. This technique uses focused light beams to achieve strong bonds. The seams produced are often smooth and durable. However, it depends on specific fabric types that can withstand laser energy. Not every project will align with these requirements, which is a valid concern. Exploring various methods reveals strengths and weaknesses that may not suit every application. It’s essential to weigh these factors before choosing a welding approach.
| Welding Method | Strength (N/5cm) | Durability (Cycles) | Cost (USD/m²) | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Welding | 150 | 1000 | 1.25 | Medical products, wipes |
| Hot Air Welding | 120 | 800 | 1.00 | Geotextiles, packaging |
| Laser Welding | 200 | 1200 | 1.50 | Automotive, fashion |
| Radio Frequency Welding | 180 | 950 | 1.75 | Medical bags, outdoor gear |
| Sewing | 75 | 600 | 0.50 | Bags, clothing |
The future of non-woven fabric welding technologies is promising. Innovations are emerging at a rapid pace. These advancements could revolutionize manufacturing processes. New techniques are likely to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Laser welding is gaining attention. This method can create precise seams and is energy-efficient. It minimizes fabric distortion, which is often a concern. However, its setup costs can be high and require training. Some manufacturers may hesitate to adopt it.
Ultrasonic welding remains popular. It generates heat through vibrations, making it effective for various applications. However, scalability can be a challenge. Many small companies might struggle with the investment. Lastly, research into biodegradable non-woven fabrics is a growing area. Sustainable materials are essential for the future. The challenge is in finding the right balance between durability and eco-friendliness.
Advancements in ultrasonic welding technology have significantly enhanced efficiency in copper wire welding and cutting applications. With the ability to complete complex bending-sealing-cutting operations in as little as one second, these systems are revolutionizing production timelines. According to industry reports, the integration of ultrasonic welding techniques can improve production speeds by up to 50%, enabling manufacturers to meet increasing demands for high throughput without compromising quality.
Moreover, the reliability of ultrasonic welding processes is evident in the high sealing strength achieved, ensuring that welded joints are resilient against air and liquid leaks. This is particularly crucial in industries where adherence to stringent safety and quality standards is a must. Research indicates that ultrasonic welding can meet the rigorous requirements posed by modern welding processes, showcasing exceptional process control and higher reliability compared to traditional methods.
Additionally, the environmental and energy-saving benefits of ultrasonic welding are noteworthy. By eliminating the need for additional welding materials, manufacturers can avoid the introduction of impurities that may compromise the integrity of the final product. The low energy consumption associated with ultrasonic welding aligns with the growing industry emphasis on sustainable practices and energy conservation. Data suggests that transitioning to this technology can lead to a 30% reduction in energy use compared to conventional welding methods, further underscoring its viability as a future-oriented solution in manufacturing.
: Look for reliability and customer reviews. Check their history and experience.
Regularly updating skills is vital. Try to learn something new every few months.
High competition is common. Many struggle with time management.
Attend events and engage on social media. Building real relationships is key.
Reflect on the experience. Learn from mistakes and adjust your approach.
Absolutely. Many people find fulfillment in new directions. Embrace the change.
Lack of motivation and constant fatigue are major indicators. Pay attention to your mental health.
Set boundaries and prioritize self-care. Schedule downtime for relaxation and hobbies.
Non Woven Fabric Welding is a crucial aspect of textile manufacturing, enabling the creation of high-quality, durable products. This article explores five essential welding methods: thermal welding, ultrasonic welding, hot air welding, laser welding, and their comparative analysis in terms of strength and durability. Understanding the science behind these techniques is vital for optimizing applications in various industries.
Each welding method offers unique advantages; for instance, ultrasonic welding is noted for its efficiency, while laser welding provides precision and versatility. As technology advances, the future of Non Woven Fabric Welding promises even more innovative solutions, enhancing capabilities and efficiency in textile production. This comprehensive overview serves as a guide for those looking to deepen their knowledge in the field of non woven fabric manufacturing.