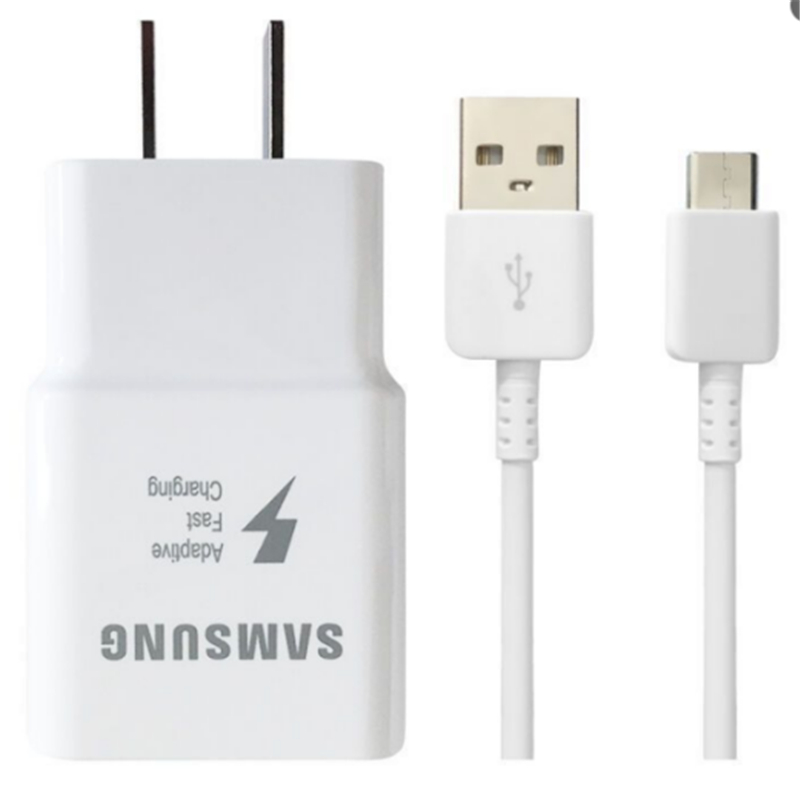
What are the unique advantages of processing the charging head with Chengguan ultrasonic welding machine?
Comparison Dimensions |
Ultrasonic welding |
Traditional welding process ( screws/hot melt/glue ) |
Welding speed |
The vibration frequency is high and the welding process is fast. A single welding point only takes a few seconds or even less, which can greatly improve production efficiency and is suitable for large-scale mass production. |
High labor ratio , slow speed and low production capacity |
Welding quality |
The welding joint has high strength, no obvious welding marks, and a beautiful and smooth appearance. It can reduce the heat-affected zone, prevent the internal electronic components of the charging head from being damaged due to overheating, and ensure performance stability. |
It is prone to defects such as pores and cracks, and may have screw holes, melt marks or glue stains , which will affect the electrical performance and service life of the charging head ;
|
Environmental performance |
No harmful gases or waste are generated, and no additional chemicals need to be added during the welding process, which is environmentally friendly and clean. |
May use glue, causing chemical pollution |
Running costs |
The equipment has a high degree of automation, reducing manual operations; no additional consumables (such as glue and screws) are required, and long-term use can significantly reduce production costs; and the equipment is easy to maintain and has a short downtime. |
It has high energy consumption, requires glue and screws , and requires continuous consumption of welding materials, resulting in high operating costs. |
Applicable scenarios |
Mass production, plastic shell fast charging head/adapter |
Small batch production, metal shell products, maintenance required |
Maintenance costs |
The equipment is relatively sophisticated and has high maintenance requirements. It requires regular maintenance by professionals. The equipment has high stability and a relatively low failure frequency. |
High rework rate due to human error (about 3-5%) |