What is Ultrasonic Welding: Working Principles, Applications and Benefits
What is Ultrasonic Welding: Working Principle, Applications and Advantages
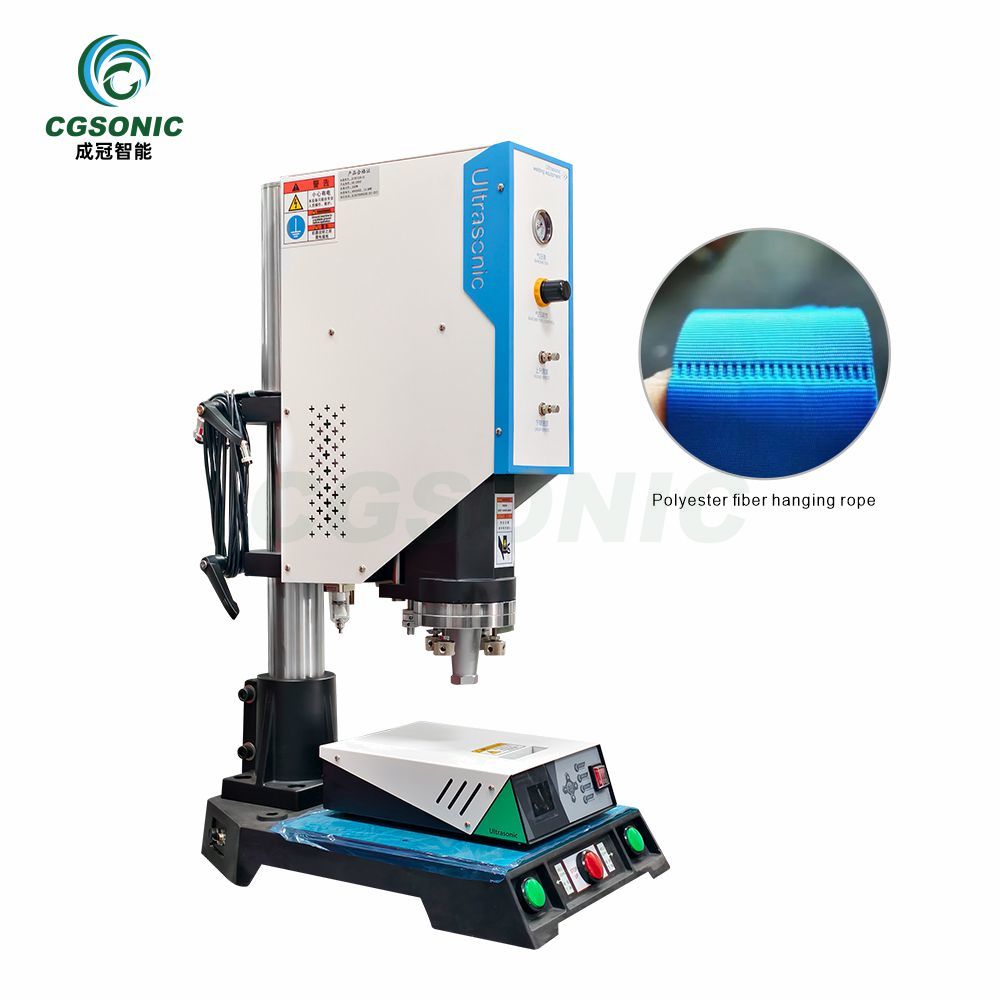
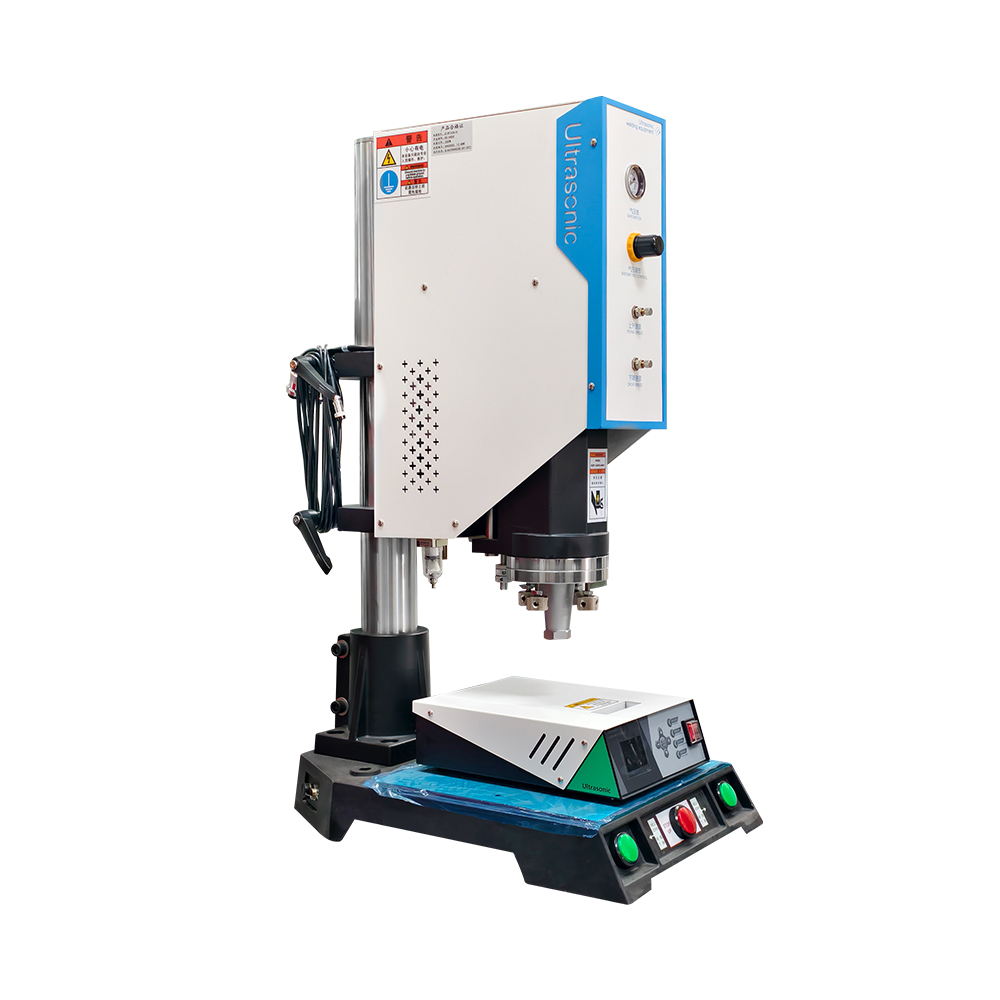
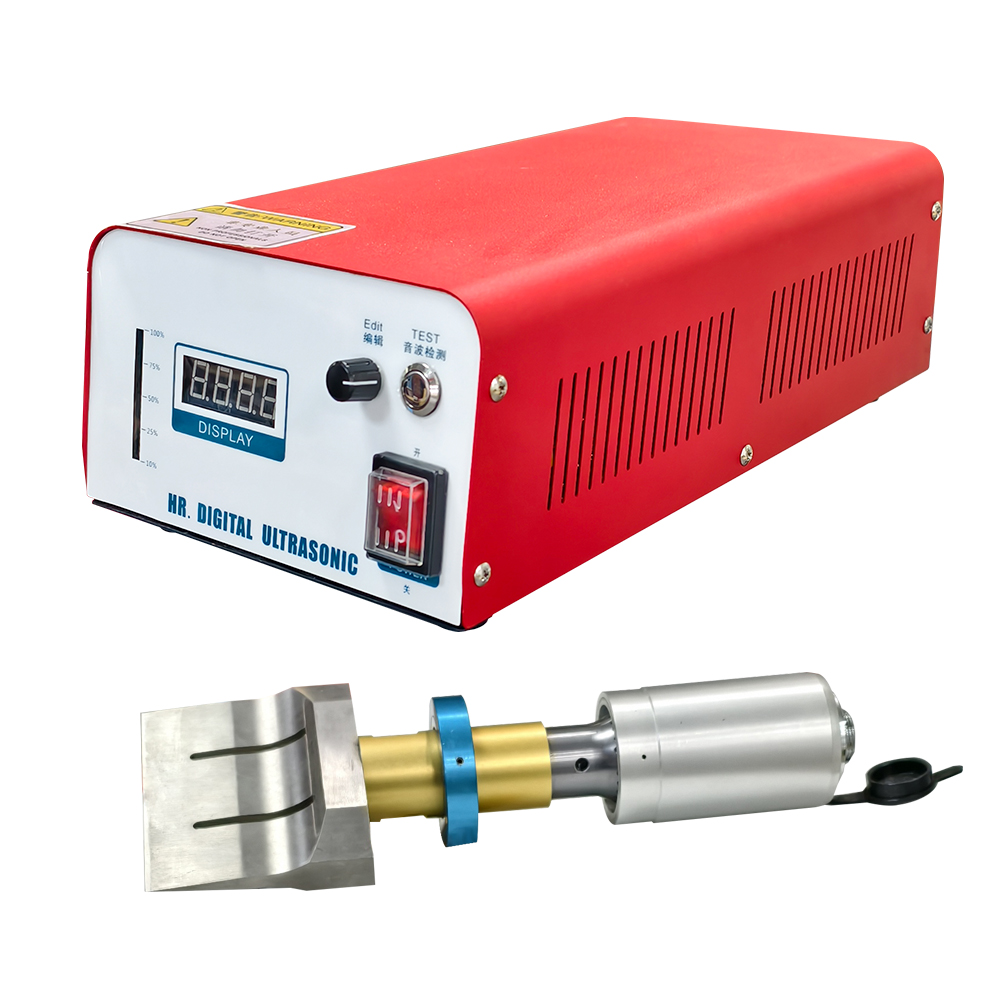
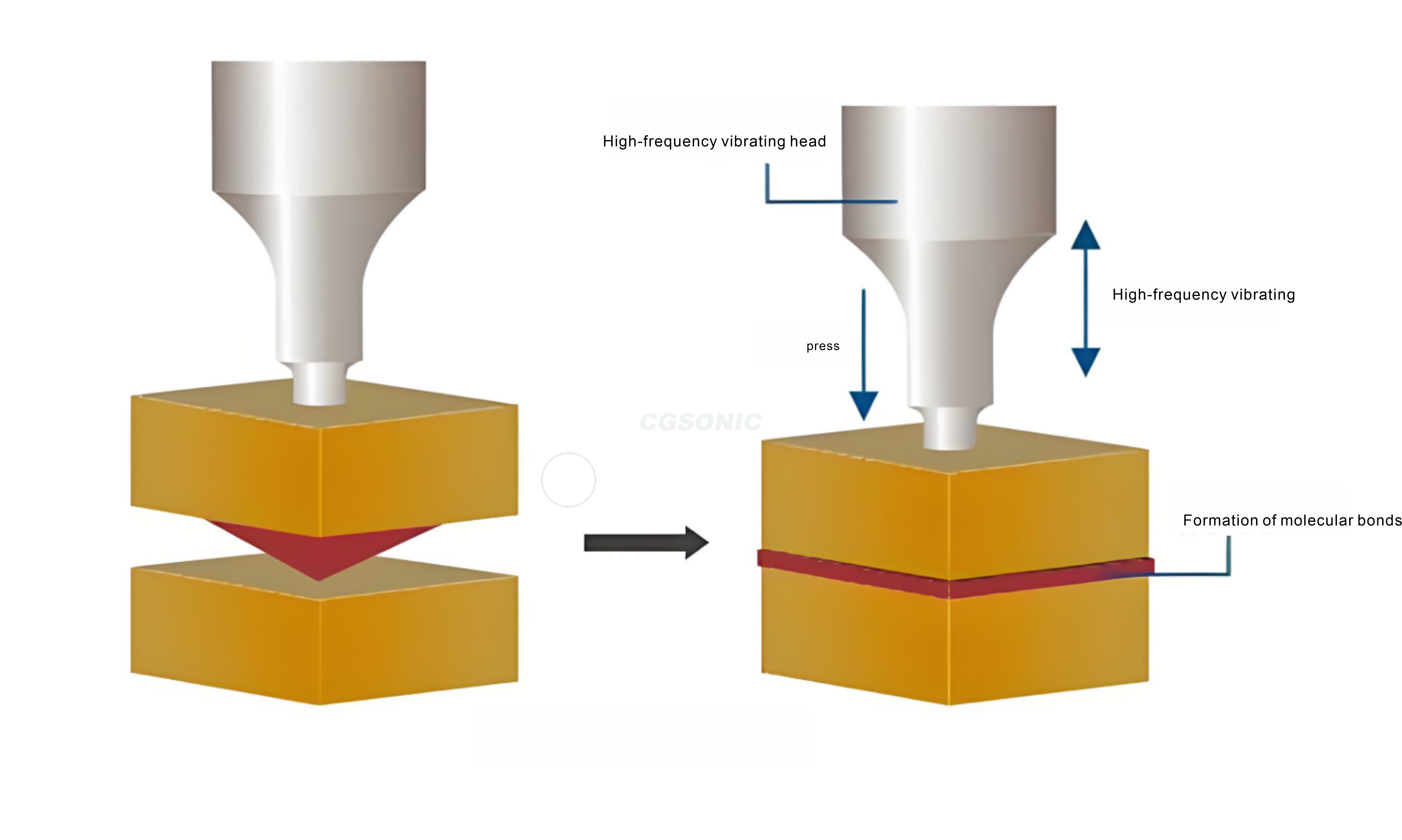
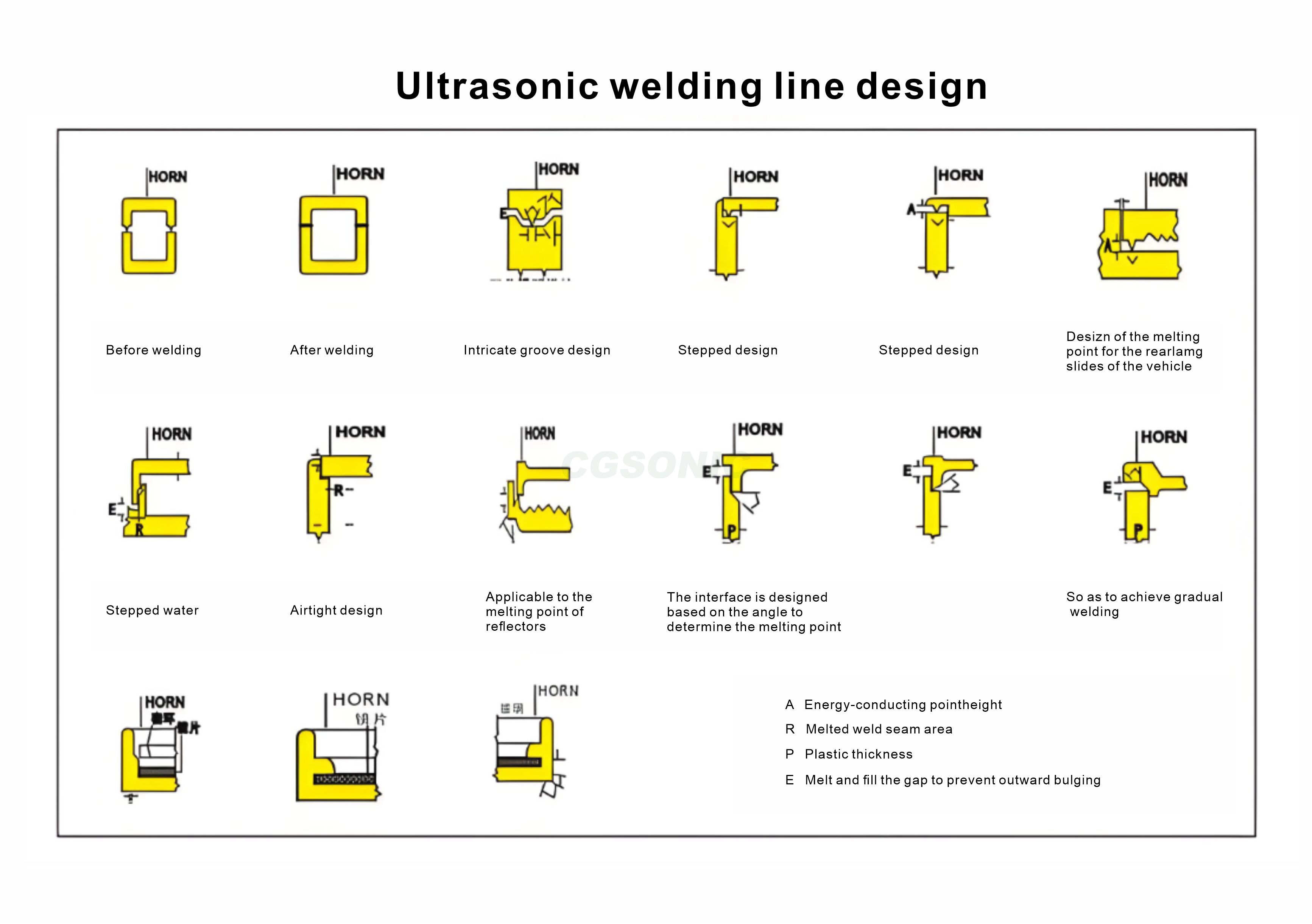
Ultrasonic welding is a technology that uses high-frequency mechanical vibrations (usually 15-70kHz) to achieve material joining. Its working principle is that the horn transmits vibration energy to the contact surface of the workpieces to be welded, causing local high-temperature plastic deformation, which forms a strong bond under pressure without additional solder.
This technology is widely used in electronics, automotive, medical and other fields, such as lithium battery tab welding, automotive wire harness connection, mask earband welding, etc.
Its advantages include: fast welding speed (usually milliseconds to seconds), high joint strength, small heat-affected zone, environmental protection without smoke and dust, and reliable joining of dissimilar materials (such as metal and plastic).