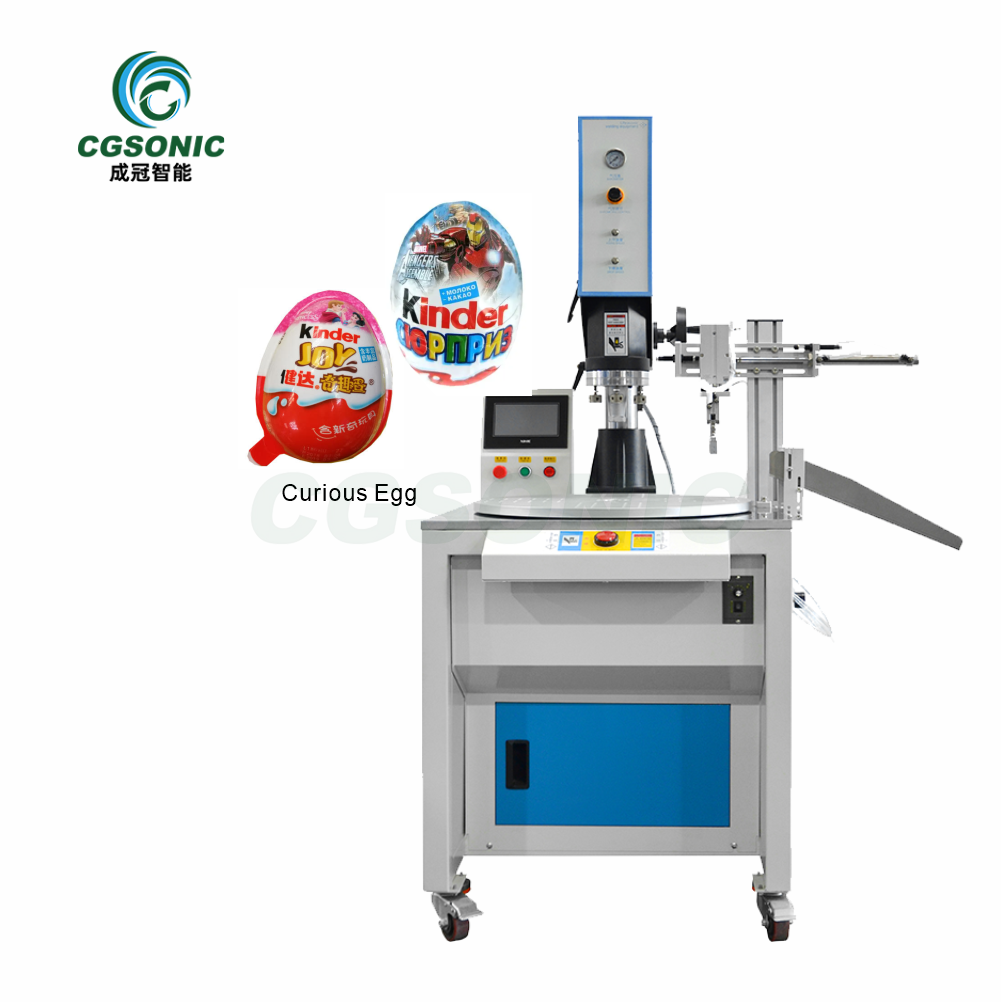
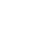What process methods does Chengguan ultrasonic welding cover?
Ultrasonic Welding is a technology that uses high-frequency vibration energy to make the surfaces of objects rub against each other to generate heat, thereby achieving welding. According to different welding principles and application scenarios, it can be mainly divided into the following methods:
1. Contact Ultrasonic Welding
Principle: The ultrasonic Welding Head (tool head) directly contacts the workpiece surface and transmits high-frequency vibration energy to the welding area, causing the material to melt locally and combine.
Features:
- The welding time is short (usually 0.1~ several seconds) and the efficiency is high.
- Suitable for materials such as thermoplastics, metal foils (such as aluminum foil, copper foil), etc.
- It is necessary to design a welding head with a specific shape (such as serrated or dotted) to enhance the welding effect.
Application scenarios:
- Plastic industry: daily necessities (such as disposable cups and containers), automotive parts (such as dashboards and headlight housings).
- Electronics industry: lithium battery tab welding and wiring harness fixing.
2. Non-Contact Ultrasonic Welding
Principle: Ultrasonic energy is transmitted through a medium (such as air or water) to make the workpieces vibrate and rub in a non-contact state to weld.
Features:
- Avoid direct contact between the welding head and the workpiece. Suitable for materials with easily damaged surfaces or high precision.
- The energy transfer efficiency is low and requires higher power support.
Application scenarios:
- Medical field: welding of sterile packaging (such as infusion bags, medical catheters) to avoid contamination.
- Microelectronics industry: welding of precision components (such as sensors and microelectronic devices).
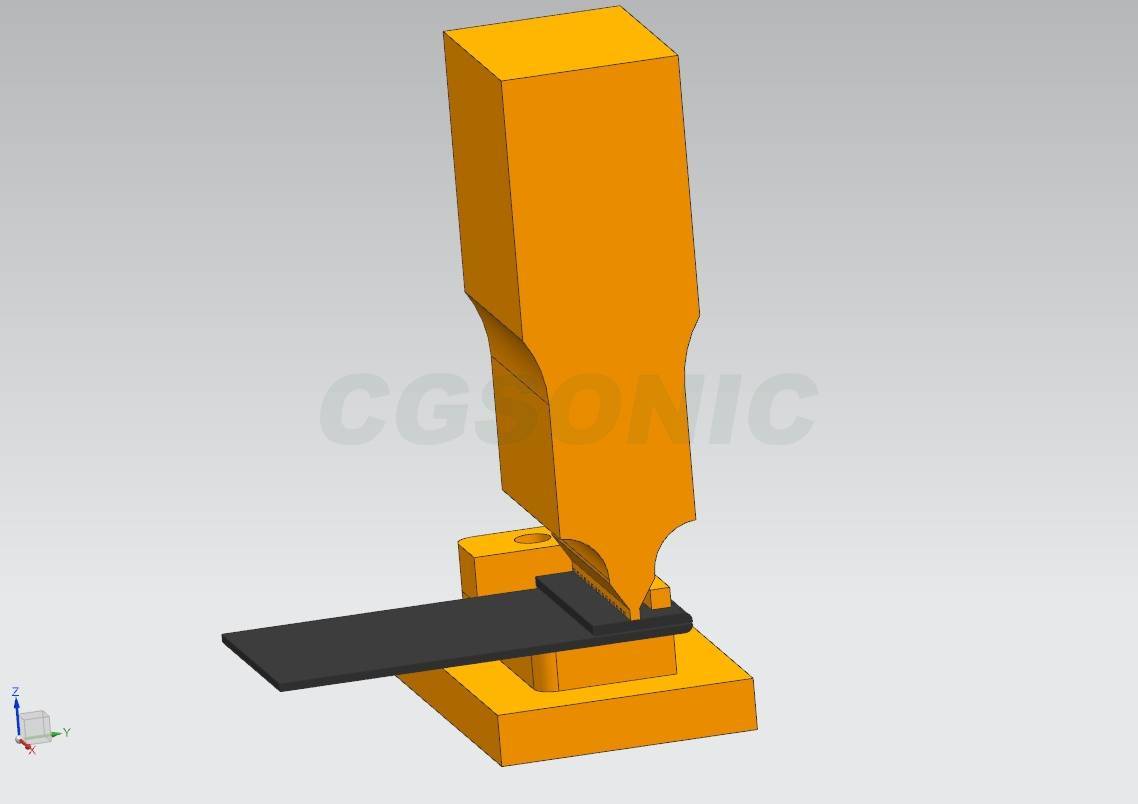
3. Ultrasonic Metal Welding
Principle: Use high-frequency vibration to destroy the oxide film on the metal surface and achieve solid-state welding (without melting the metal) through intermolecular bonding.
Features:
- The welding process has low temperature and is not prone to thermal deformation and oxidation.
- Can weld dissimilar metals (such as aluminum and copper, aluminum and steel).
Application scenarios:
- Battery industry: welding of power battery pole pieces and tabs.
- Electronic appliances: welding of motor windings and connector terminals.
4. Ultrasonic Plastic Welding
Principle: Ultrasonic vibration generates friction heat on the plastic contact surface, causing the material to melt and solidify.
Features:
- The welding strength is high and the sealing is good, which can achieve watertight or airtight effect.
- The vibration frequency and pressure need to be adjusted according to the type of plastic (such as ABS, PC, PP).
Application scenarios:
- Automobile industry: bumpers, dashboards, air conditioning parts.
- Packaging industry: hose sealing, plastic bottle label welding.
5. Ultrasonic Wire Harness Welding
Principle: Multiple strands of wires or wire harnesses are welded together through ultrasonic vibration extrusion to form a conductive joint.
Features:
- After welding, it has good conductivity and high tensile strength.
- No solder or flux is required, environmentally friendly and highly reliable.
Application scenarios:
- Automobile wiring harness: connection of door wiring harness and engine wiring harness.
- Consumer electronics: terminal welding of headphone cables and charging cables.

6. Ultrasonic Spot Welding
Principle: Through the local contact of the welding head, single-point or multi-point welding is formed on the workpiece, similar to the "spot welding" effect.
Features:
- Precise positioning, suitable for welding of small size or complex structures.
- It can quickly weld multiple welding points on the same workpiece.
Application scenarios:
- Textile industry: welding of non-woven mask ear straps and fixing of clothing accessories.
- Medical consumables: welding of syringe parts and filter devices.
Summary
There are many ways to weld ultrasonic welding, and the core differences lie in the energy transfer method, material type, and welding structure. The selection should be based on the workpiece material (plastic, metal, or composite material), welding strength requirements, production efficiency, and other factors. For example, plastic welding focuses more on the welding effect, while metal welding focuses on solid-state bonding and conductivity. With the development of technology, the application of ultrasonic welding in new energy, microelectronics and other fields is also expanding.